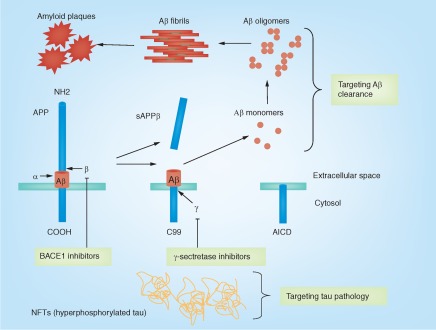
Figure 3. . Aβ production and clearance, neurofibrillary tangles and current drug development strategy to treat Alzheimer's disease.
The APP can undergo proteolytic processing by secretases. In the amyloidogenic pathway, APP is first cleaved by β-secretase (BACE1), releasing an ectodomain (sAPPβ) and retaining the last 99 amino acids of APP (C99) within the membrane. C99 is subsequently cleaved 38–43 amino acids from the amino terminus to produce Aβ, by the γ-secretase. In contrast, in the nonamyloidogenic pathway, cleavage by α-secretase occurs within the Aβ domain, thereby preventing the generation and release of the Aβ peptide. Current drug development includes targeting BACE1 and γ-secretase to reduce Aβ production. In addition, targeting Aβ clearance aims to increase Aβ turnover in the brain; targeting tau pathology aims to reduce tau toxicity in the brain.
α: α-cleavage site; AICD: APP intracellular domain; β: β-cleavage site; γ: γ-cleavage site.