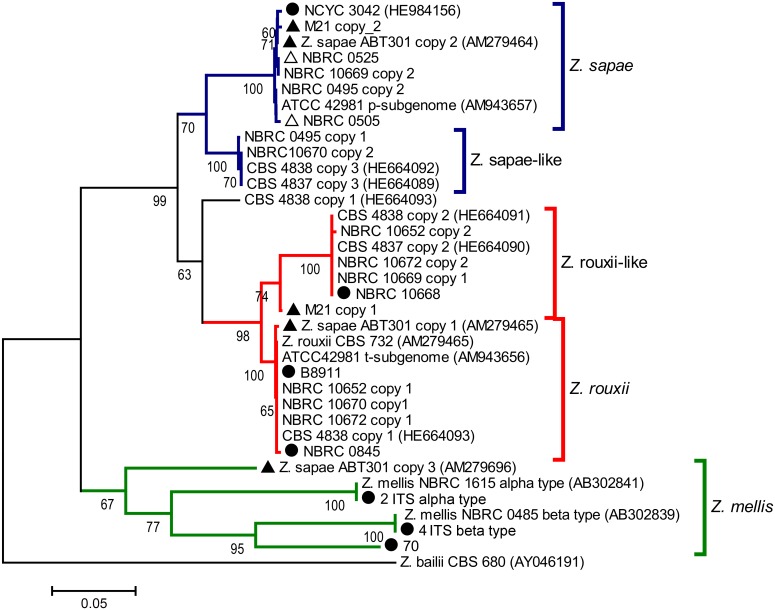
Fig 2. Phylogenetic relationships within the Z. rouxii complex inferred from ITS sequences.
This phylogeny was inferred through the Neighbor-Joining method using the ITS sequence of Z. bailii CBS 680T (GenBank accession number AY046191) as outgroup. The percentage values of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (10,000 replicates) are shown next to the branches (only values higher than 60% are reported). The evolutionary distances were computed using the Tamura-Nei method [47]. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. Z. rouxii and Z. rouxii-like clades are colored in red, Z. mellis clade in green, and Z. sapae and Z. sapae-like clades in blue. Black triangles represent strains with homogeneous 26S rDNA D1/D2 domains and heterogeneous ITS regions. Black circles indicate strains without any rDNA heterogeneity. White triangles indicate strains with heterogeneous 26S rDNA D1/D2 domains and homogeneous ITS rDNA regions.