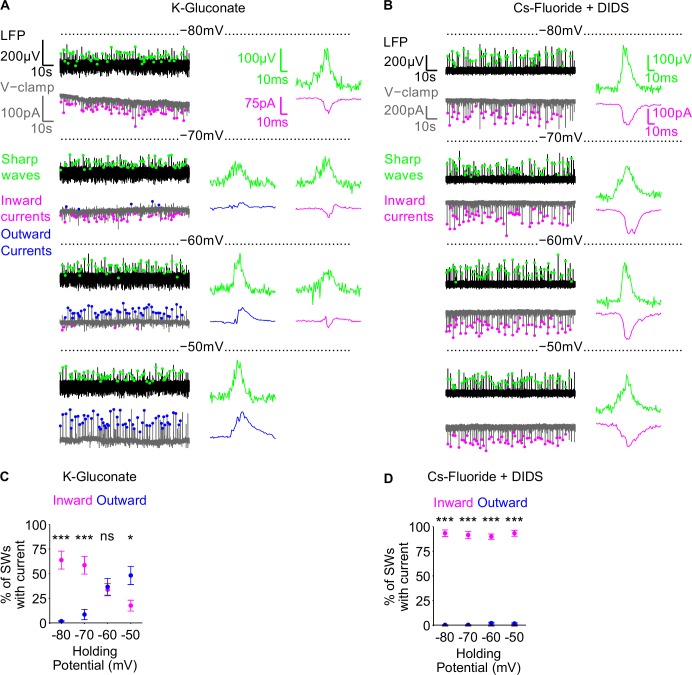
Fig 4. Fluoride-based intracellular pipette solution can block spontaneous IPSCs during hippocampal sharp waves.
A-B) Example traces of an experiment using K-Gluconate (A) and Cs-Fluoride +DIDS intracellular pipette solutions (B) are shown in the left panels. In each case, the LFP (black) was recorded whilst holding the cell at 1 of 4 different holding potentials (-80mV, -70mV, -60mV and -50mV) (grey). Inward and outward PSCs, detected during sharp waves (green dots), are demarked by magenta and blue dots respectively. Individual example sharp waves and PSCs, at the different holding potentials, are shown in the right panels. C-D) Group data showing the percentage of sharp waves for which a concomitant inward (magenta) or outward (blue) PSC was detected, at the different holding potentials, in K-Gluconate (C) and Cs-Fluoride + DIDS (D) intracellular pipette solutions. Data are plotted as mean ± SEM.