Figure 1.
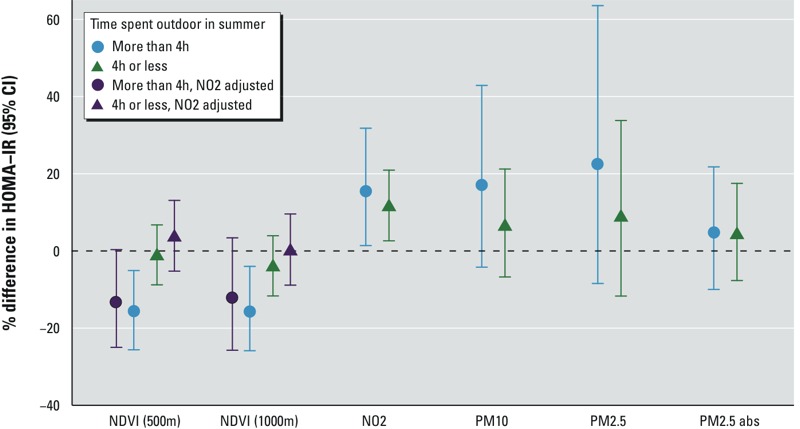
Stronger effect estimates in adolescents spending more time outside in summer. GAMs were adjusted for study area, cohort, sex, age, BMI, smoking by the adolescent, paternal and maternal education levels, secondhand smoke in the home, physical activity, pubertal state, city-specific equivalent net income tertiles. p-Values for the interaction with time spent outside in summer: NDVI (500 m): p = 0.043, NDVI (1,000 m): p = 0.124, NO2: p = 0.504, PM10: p = 0.885, PM2.5: p = 0.784, PM2.5 absorbance: p = 0.306.
