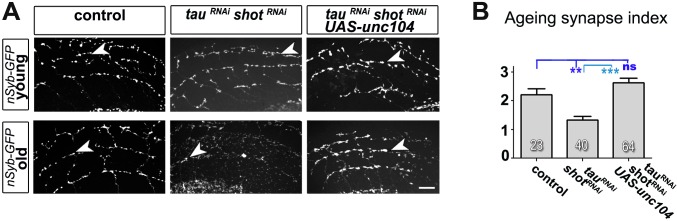
Figure 5. Defects in kinesin-3 function mediate synaptic deficits in shot-tau mutant neurons.
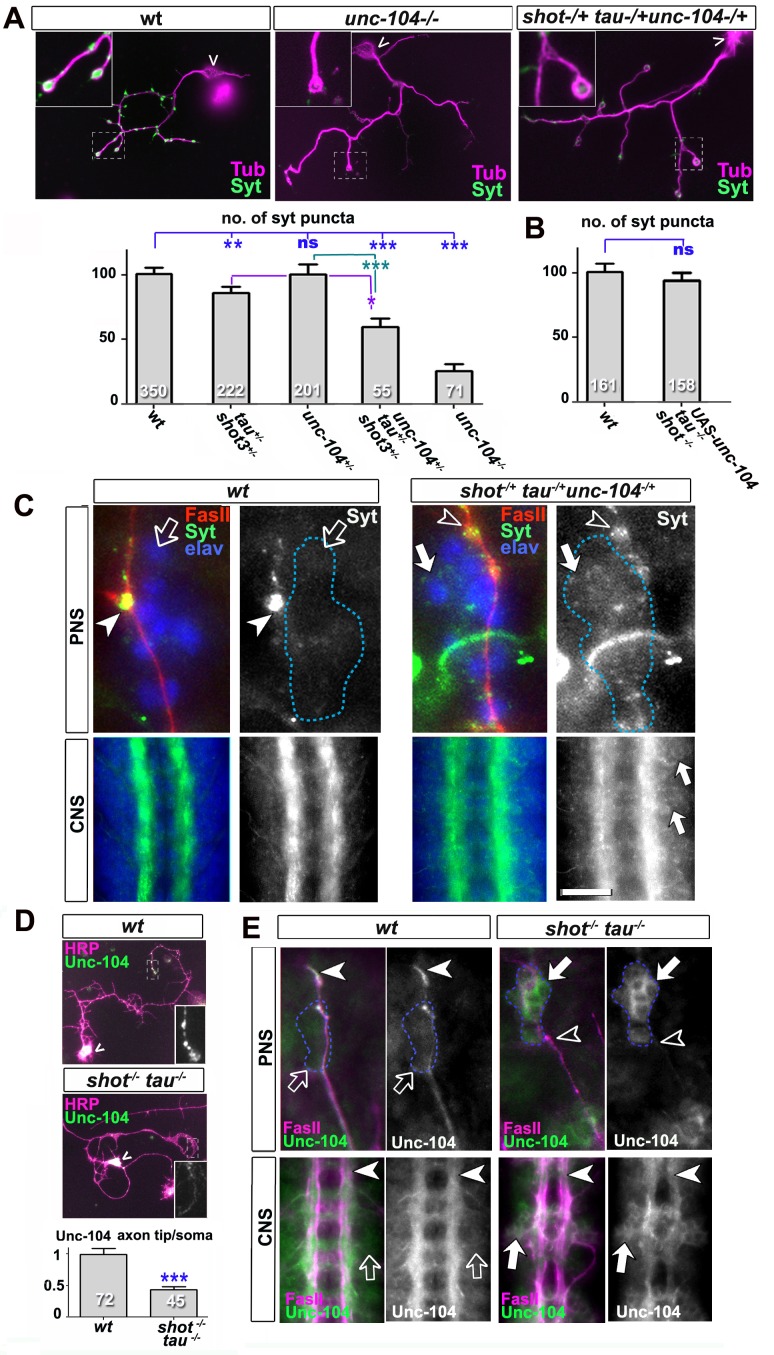
Shot and Tau interact with Unc-104 and regulate its subcellular distribution. (A) Primary Drosophila neurons at 2 DIV, obtained from embryos which were wildtype, homozygous for unc104imac170 (unc104-/-), or triple-heterozygous for shot3 tauMR22 unc104imac170 mutations (shot+/- tau+/-unc104+/-), co-stained with antibodies against tubulin (Tub, magenta) and Syt (green). The graph shows the quantification of the data including also unc104-/+ and shot-/- tau-/-controls. (B) Quantification of Syt puncta in two day old neurons, obtained from embryos that were wildtype or shot-/- tau-/- with elav-Gal4 driven expression of UAS-unc-104 (compare Figure 1D). (C) The dorsal peripheral nervous system (PNS) and the central nervous system (CNS) of wildtype and shot3 tauMR22 unc104imac170triple heterozygous embryos at late stage 16 (stages according to Campos-Ortega and Hartenstein, 1997) stained for Syt (green), FasII (red in upper panel) and the pan-neuronal nuclear marker Elav (blue); for illustration of the imaged tissue see Figure 2-figure supplement 1. The nascent NMJ at the tip of the inter-segmental motornerve (red in upper panels) in wildtype contains high levels of Syt (arrowheads) whereas the somata of sensory neurons (blue; demarcated by dashed lines) contain low levels (open arrows); in shot3 tauMR22 unc104imac170triple heterozygous embryos the somata of sensory neurons have high levels of Syt (arrows), whereas there is only little staining at the nerve tip (open arrowhead). In the ventral nerve cord of wildtype (lower panels), Syt is confined to the neuropile (synapse containing CNS compartment; arrowheads) and excluded from the cortex (compartment with the cell bodies of inter- and motorneurons); in the ventral nerve cord of shot3 tauMR22 unc104imac170triple heterozygous embryos, there are segmental groups of cell bodies displaying higher Syt levels (arrows). (D) Primary Drosophila neurons at 2 DIV, obtained from wildtype (wt) and tau-shot mutant embryos, stained with antibodies against pan-neuronal HRP (magenta) and Unc-104 (green); Unc-104 in distal axon segments (emboxed and magnified in insets) is enriched in wildtype but much weaker in shot-tau mutant neurons (chevrons indicate neuronal somata). Data were quantified as average intensity of Unc-104 at the distal end of the axon divided by the average intensity at the soma. (E) Upper and lower panels show the same locations of late stage 16 embryos as shown in C, but taken from wildtype and shot-tau mutant embryos, stained for FasII (magenta) and Unc-104 (green). Note the stark decrease of Unc-104 at the end of motor nerves (open versus white arrow heads) and the unusual accumulations of Unc-104 in the cell bodies of sensory neurons as well as in the CNS cortex in shot-tau embryos (open versus white arrows). In all graphs, the number of assessed neurons is indicated in each bar; ***PMW<0.001; *PMW<0.05; ns, not significant PMW>0.05; scale bars: 18 μm in A, 5 μm in C/PNS, 35 μm in C/CNS, 15 μm in D and E/PNS, 35 μm in E/CNS. A statistics summary of the data shown here is available in Figure 5—source data 1.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.14694.021