Figure 1. Decreased functional connectivity (FC) between the right temporo-parietal junction (rTPJ) and bilateral sensorimotor regions in patients with functional movement disorders (FMD).
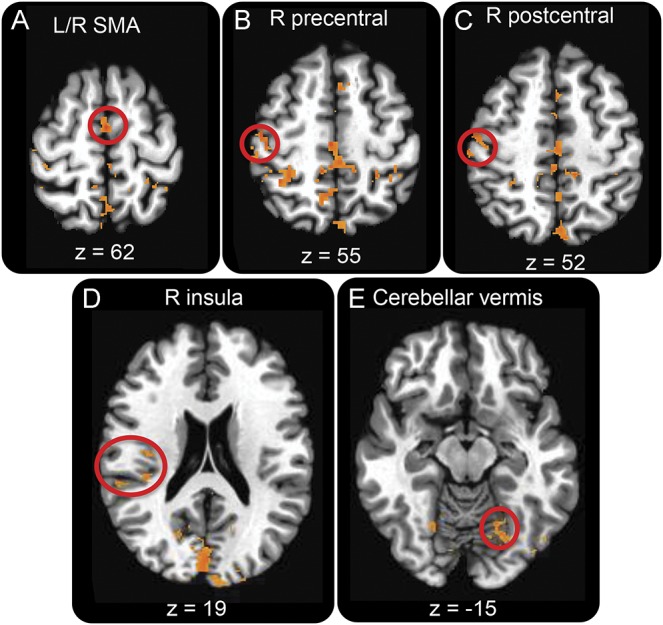
Maps demonstrate group differences in rTPJ resting-state FC between patients with FMD and healthy controls. Images show decreased FC in patients with FMD between the rTPJ (seed) and the (A) bilateral supplementary motor area (SMA) (circled), (B) right precentral gyrus (circled), (C) right postcentral gyrus (circled), (D) right insula (circled), and (E) cerebellar vermis (circled). The threshold for display was set at p < 0.02; cluster size >28 voxels.
