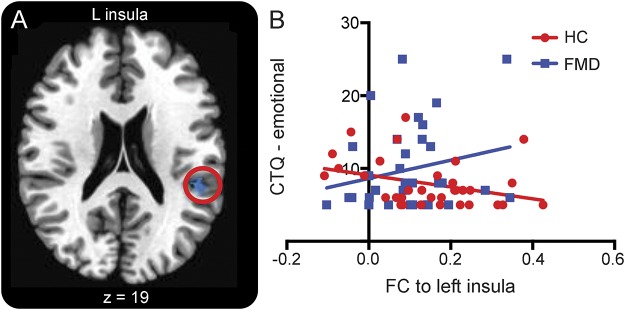
Figure 2. Childhood emotional trauma differentially affects right temporo-parietal junction (rTPJ) functional connectivity (FC) in patients with functional movement disorders (FMD).
Connectivity map and scatterplot demonstrate group differences in correlation between rTPJ resting-state FC to left insula and levels of childhood emotional trauma. Connectivity map (A) and adjacent scatterplot (B) demonstrate rTPJ FC in patients with FMD compared to healthy controls (HCs) with increasing levels of childhood emotional abuse. Scatterplot shows the relationship between mean z connectivity values and Childhood Trauma Questionnaire emotional abuse subscore for patients and HCs.