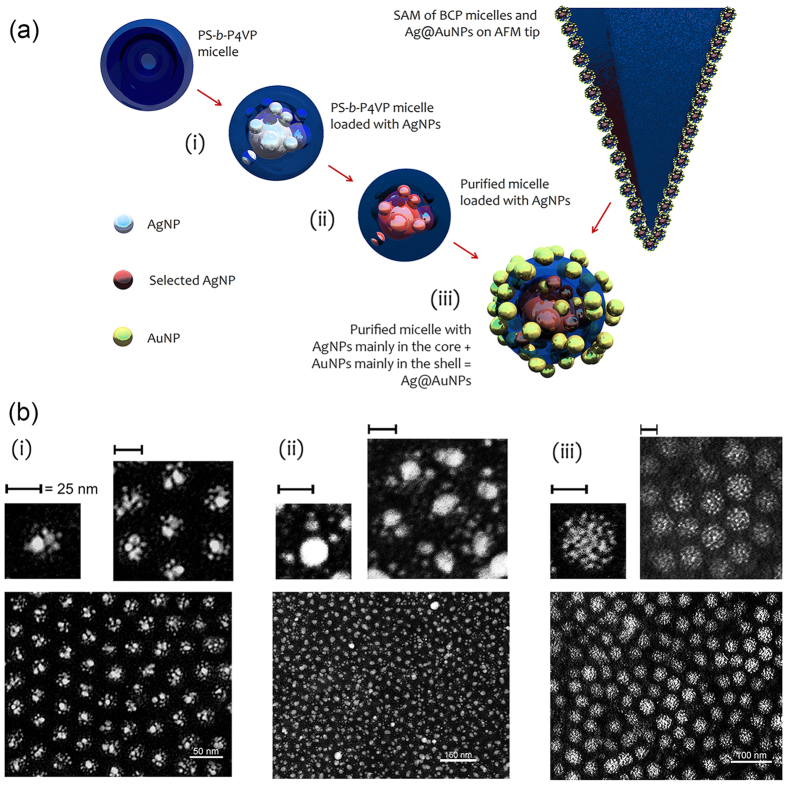
Figure 1. Schematic process of SAM coating of Si-AFM tip by BCP micelles loaded with AgNPs and Ag@AuNPs.
(a) In step (i), PS-b-P4VP micelles are loaded with AgNPs, mainly in the core of P4VP copolymer42. (ii) Next, overgrowth of AgNPs in presence of an excess of Ag+ in solution, produces bigger NPs; Ag-BCP nanocomposites are purified by density gradient centrifugation to select micelles with larger NPs in the core. In the next step (iii), Au precursor is added to the solution of micelles preloaded with AgNPs; AuNPs, formed with excess of NaBH4, were evident in the BCP micelles by EDX analysis (Fig. S1) and UV-vis spectroscopy (Fig. 2), and morphologically evident in the PS shell at TEM inspection reported in panel (b). Therefore, we tentatively describe this structure as consisting of AgNPs mainly in the P4VP core and AuNPs mainly in the PS shell ( as Ag@AuNPs). Finally, both solutions of BCP with AgNPs or Ag@AuNPs are used to coat Si-AFM tips by dip coating. (b) TEM micrographs (inverted colormap) of the three steps of the process depicted in panel (a). In particular, the modification of the size of the NPs, evident from the comparison of the consecutive SAMs spin-coated on glass, pointed out the formation of AgNPs of 15–20 nm surrounded by smaller Ag seed satellites in the P4VP core (ii). An outer shell that we ascribe to tiny AuNPs (
as Ag@AuNPs). Finally, both solutions of BCP with AgNPs or Ag@AuNPs are used to coat Si-AFM tips by dip coating. (b) TEM micrographs (inverted colormap) of the three steps of the process depicted in panel (a). In particular, the modification of the size of the NPs, evident from the comparison of the consecutive SAMs spin-coated on glass, pointed out the formation of AgNPs of 15–20 nm surrounded by smaller Ag seed satellites in the P4VP core (ii). An outer shell that we ascribe to tiny AuNPs (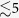 nm) appears in (iii) as described in the main text. Top insets are magnified regions of the corresponding bottom scans. Scalebars are 50, 150 and 100 nm in (i), (ii) and (iii), respectively, whereas scalebar = 25 nm in all top insets.
nm) appears in (iii) as described in the main text. Top insets are magnified regions of the corresponding bottom scans. Scalebars are 50, 150 and 100 nm in (i), (ii) and (iii), respectively, whereas scalebar = 25 nm in all top insets.