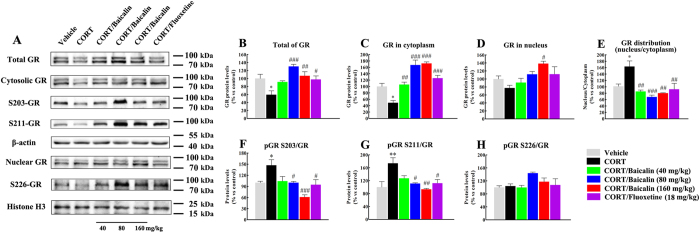
Figure 3. Effects of baicalin (40, 80 and 160 mg/kg) on the levels of GR and phosphorylated GR in the CORT model of anxiety/depression.
Representative western blots of GR protein expression are shown (A). The graphs show quantification of total GR protein level (B), GR protein level in the cytoplasm (C), GR protein level in the nucleus (D), GR distribution (E), GR phosphorylation at S203 (F) and S211 (G) in the cytoplasm, and GR phosphorylation at S226 (H) in the nucleus. Baicalin significantly increases the total GR protein level and the cytoplasmic GR protein level, normalizes the GR distribution, and decreases the levels of pSer203/GR and pSer211/GR in the cytoplasm in the CORT model of anxiety/depression. All gels were run under the same experimental conditions and were cropped based on the molecular weight of the target protein (full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figs S2–S9). The boundary between the gels is delineated by a black line. Data are expressed as means ± S.E.M (n = 6–8 mice/group). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs vehicle. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 and ###P < 0.001 vs CORT model.