Figure 2. Estimated Impact of BIC on Annual Breakfast and Lunch Participation Rates: Elementary and Middle Schools.
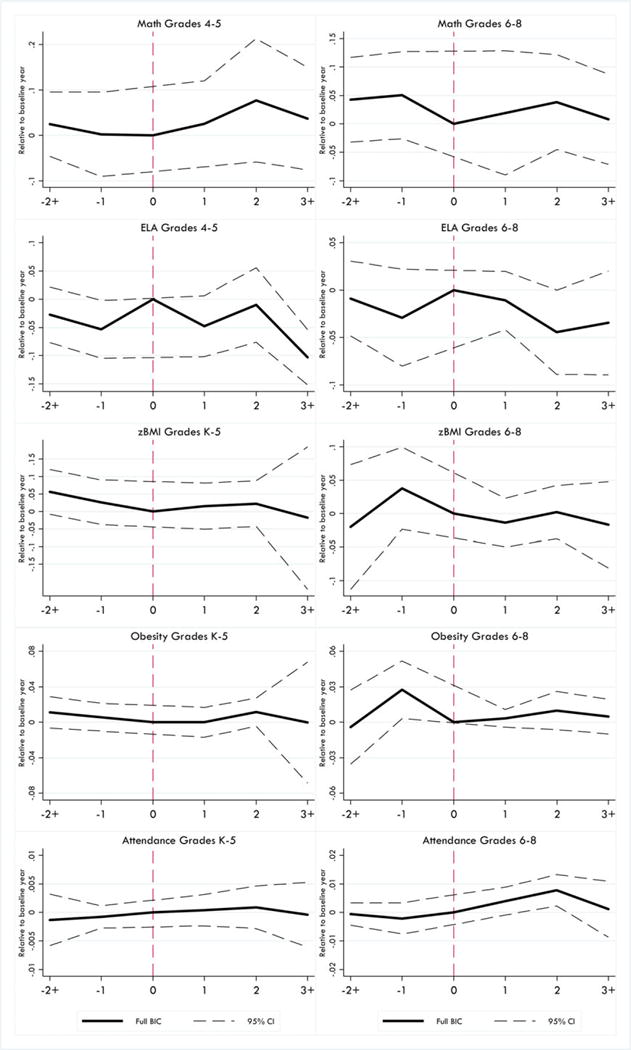
Notes: Event study coefficients from school-level regressions. Meals program participation is measured as average daily meals served divided by ADA. All models include school and year effects. Covariates include total school enrollment, percent ELL, percent receiving special education services, percent of students by race/ethnicity, percent female, percent eligible for free meals, and percent eligible for reduced price meals. Separate indicator variables are included for three categories of BIC schools: (1) those that offered BIC to fewer than 25 percent of all classrooms; (2) those that offered BIC to 25 percent or more of classrooms, but did not offer it schoolwide; (3) those that reported offering BIC schoolwide. These category variables are interacted with indicators for years before and after BIC adoption. Only results for categories (2) and (3) are pictured. Dashed and dotted lines represent a robust 95 percent confidence interval.
