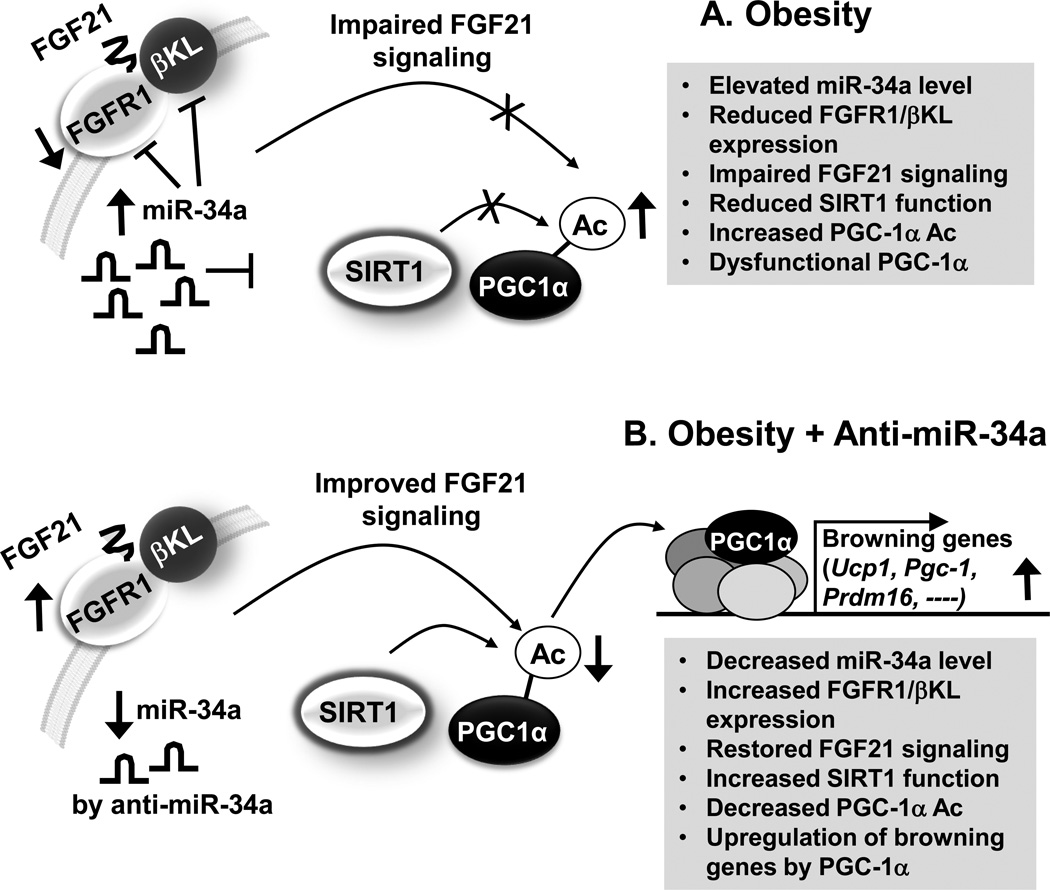
Fig. 2. Role of the miR-34a/βKL/FGF21 axis in adipose tissue.
(A) In diet-induced obese mice, elevated miR-34a in adipocytes attenuates FGF21 signaling, at least in part, by directly targeting both components of the FGF21 receptor complex, both FGFR1 and βKL, and also by targeting SIRT1 deacetylase. Decreased SIRT1 function results in increased acetylation levels of PGC1-α and subsequently decreased transcriptional activity of PGC1-α in regulation of PGC-1α target browning-related genes. (B) Downregulation of elevated miR-34a in obese mice by treatment with anti-miR-34a improves FGF21 signaling, at least in part, by increasing expression of the FGF21 receptor complex, both FGFR1 and βKL, and also increases expression and activity of SIRT1, which contributes to deacetylation of PGC-1α and induction of PGC-1α target browning-related genes.