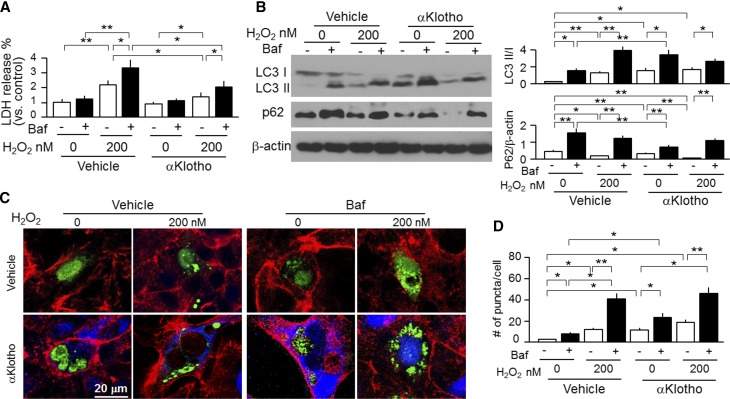
Figure 8.
αKlotho upregulates autophagy and protects kidney cell against oxidative stress–induced cell injury. OK cells were treated with H2O2 with or without Baf (200 nM). In addition, recombinant αKlotho protein was added to examine whether αKlotho suppresses cell injury induced by H2O2. (A) LDH in supernatants released from OK cells was used for assessment of cell injury. (B) Protein expression of LC3-I, LC3-II, and p62 protein in OK cells. (Left panel) Representative immunoblots for LC3-I and LC3-II, p62, and β-actin protein. (Right panel) Summary of immunoblots from three independent experiments. Data are expressed as means±SDs. (C) Representative immunocytochemistry for αKlotho (blue), LC3 (green), and phalloidin (red) in OK cells. OK cells were seeded on coverslips and transfected with GFP-LC3 plasmid. After 24 hours of transfection, cells were treated with H2O2 and/or Baf. Vehicle (upper panel) or recombinant αKlotho protein (0.4 nM; lower panel) was added to examine whether αKlotho suppresses cell injury induced by H2O2 in the presence of αKlotho or vehicle for control for 24 hours. Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) Quantification of the number of GFP-LC3 punctae per cell in OK cells (100 cells analyzed per sample). Results represent as means±SDs from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls test. Statistical significance was accepted when *P<0.05; **P<0.01 between two groups.