Fig. 3.
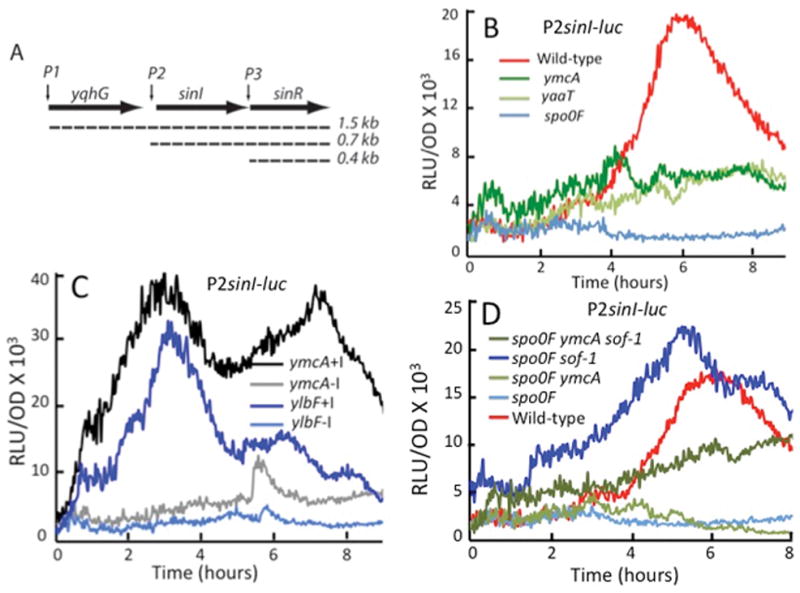
YlbF, YmcA and YaaT act positively on the rate of sinI transcription by stimulating the production of Spo0A-P. (A) A transcription schematic of the sin locus. (B) The effect of ylbF, ymcA and yaaT knockouts on transcription from a P2sinI-luc reporter construct. (C) Effects of IPTG induction of the sad-67 mutant form of spo0A on expression from the P2sinI promoter in the presence of ymcA and ylbF knockouts. The lines labeled +I and −I indicate the presence and absence of IPTG. (D) Effects of the sof-1 allele of spo0A on expression from P2sinI in the presence of spo0F and ymcA knockouts. Strains used were as follows. (B) wild-type PsinI-luc (BD7817), ΔymcA PsinI-luc (BD7821), ΔyaaT PsinI-luc (BD7820). (C) ΔymcA sad-67 PsinI-luc (BD7842), ΔylbF sad-67 PsinI-luc (BD7843). (D) wild-type PsinI-luc (BD7817), Δspo0F PsinI-luc (BD7853), Δspo0F sof-1 PsinI-luc (BD7854), Δspo0F sof-1 ΔymcA PsinI-luc (BD7855), Δspo0F ΔymcA PsinI-luc (BD7856). The bacteria were grown in MSgg and all the strains were constructed in the 3610 background.
