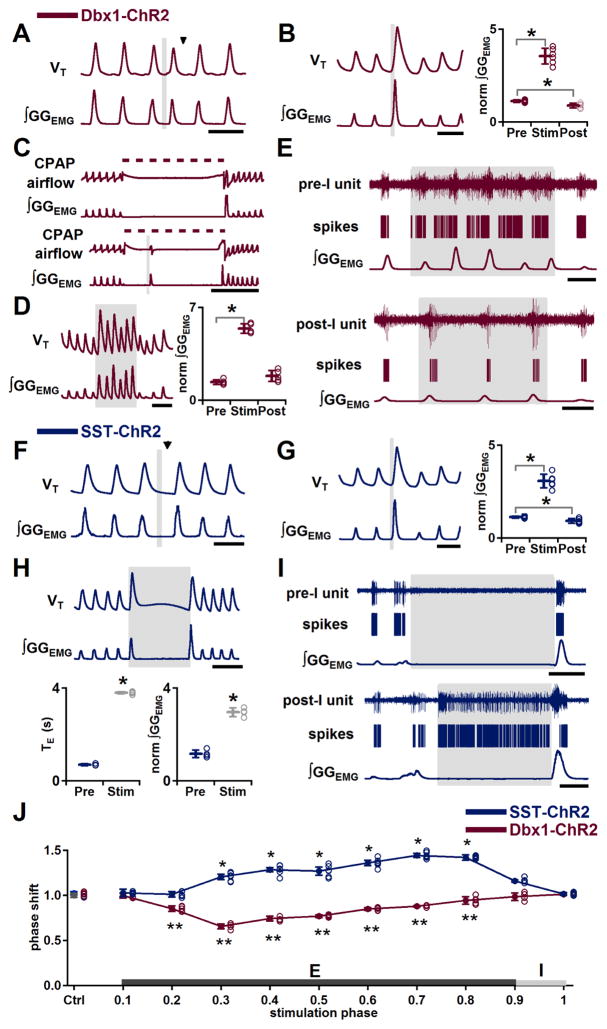
Figure 3.
Effects of bilateral preBötC photostimulation on burst timing and motor output pattern in Dbx1-ChR2 and SST-ChR2 mice. (A–E) In Dbx1-ChR2 mice, bilateral preBötC photostimulation is excitatory. A, Ectopic inspiratory burst induced by bilateral preBötC SPP during midexpiration. Black arrowhead indicates expected onset of inspiratory burst following photostimulation. Scale bar, 1 s. B, Left: Augmented inspiratory bursts induced by bilateral preBötC SPP in early inspiration. Scale bar, 1 s. Right: Bilateral preBötC SPP effects on normalized (norm) ∫GGEMG prestimulation (Pre), during stimulation (Stim) and poststimulation (Post) (*, P<0.05; n=6). C, During an inflation-induced apnea (top), bilateral preBötC SPP broke apnea for pulse duration (bottom). Dotted line represents CPAP (8 cm H2O). Scale bar, 5 s. D, Left: Bilateral preBötC LPP produced augmented inspiratory bursts. Scale bar, 2 s. Right: Bilateral preBötC LPP effects on norm ∫GGEMG Pre, during Stim and Post (*, P<0.05; n=5). E, Firing patterns of preinspiratory (pre-I; top) and postinspiratory (post-I; bottom) preBötC neurons in response to bilateral preBötC LPP in Dbx1-ChR2 mice. Scale bar, 1 s. (F–I) In SST-ChR2 mice, bilateral preBötC photostimulation evoked phase-dependent excitatory or inhibitory responses. F, Bilateral preBötC SPP during midexpiration depressed inspiratory motor output or lengthened expiratory duration. Black arrowhead indicates the expected onset of inspiratory burst following photostimulation. Scale bar, 1 s. G, Left: Augmented inspiratory bursts induced by bilateral preBötC SPP in early inspiration. Scale bar, 1 s. Right: Bilateral preBötC SPP effects on norm ∫GGEMG Pre, during Stim and Post (*, P<0.05; n=6). H, Top: Apneas produced by bilateral preBötC LPP. Scale bar, 2 s. Bottom: Left: Duration of bilateral preBötC LPP-induced apnea compared to TE of the previous cycle (*, P<0.05; n=4). Right: Amplitude of the GGEMG burst induced by bilateral preBötC LPP compared to ∫GGEMG of previous cycle (*, P<0.05; n=4). I, Firing patterns of preinspiratory (pre-I; top) and postinspiratory (post-I; bottom) preBötC neurons in response to bilateral preBötC LPP in SST-ChR2 mice. Scale bar, 1 s. J, Phase response curves show that bilateral preBötC SPP in SST-ChR2 mice (blue; n=6) led to phase delays and bilateral preBötC SPP in Dbx1-ChR2 mice (red; n=5) led to phase advances. *, ** comparisons versus control phase shift (Ctrl), P<0.05. Error bars represent mean±SD.