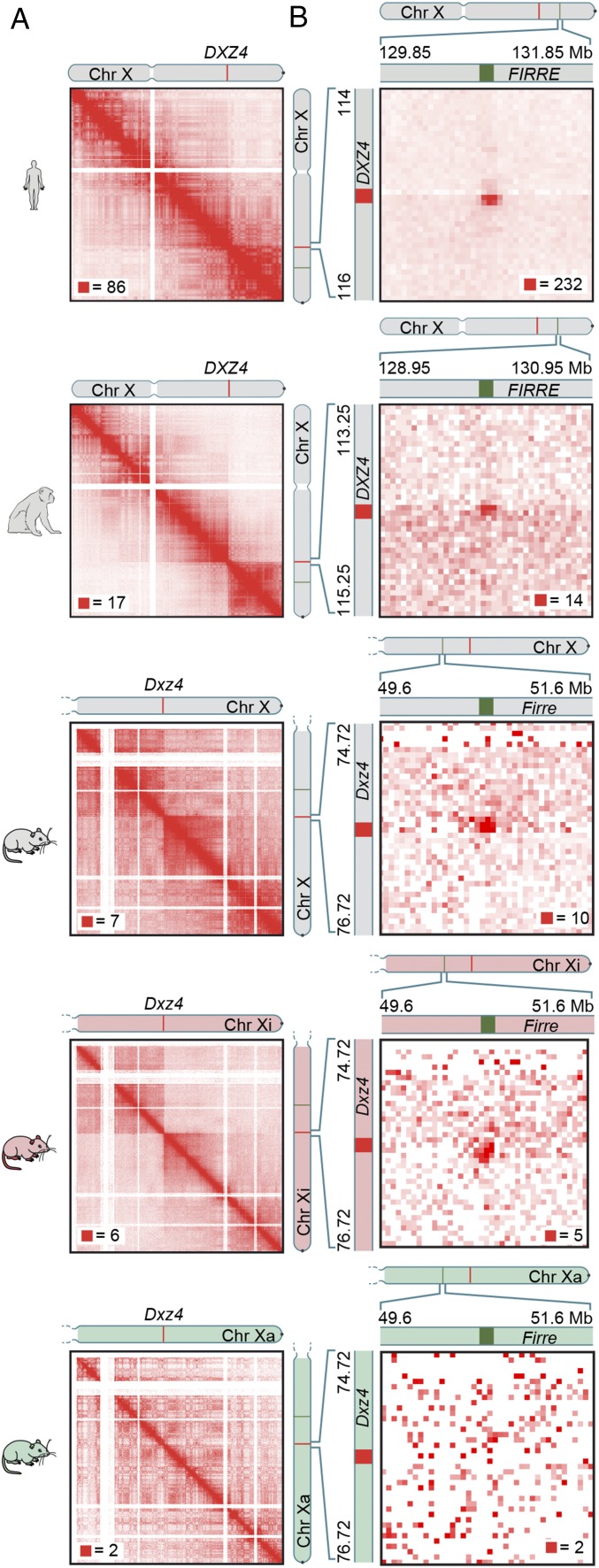
Fig. 1.
The Xi chromosome superstructure is conserved across human, rhesus macaque, and mouse. (A) Superdomains on the Xi chromosome are conserved across human, rhesus macaque, and mouse. The boundary of the superdomains lies at DXZ4 and its orthologs. In diploid Hi-C maps of mouse, the superdomain is seen only on the Xi chromosome. (Resolution: 100 kb.) For all contact maps, the color scale of each map goes from 0 (white) to red, whose value is given by the red square in each map. The chromosome icons are colored gray to indicate unphased maps of the X chromosome, in which data from both the Xi and Xa chromosomes are superimposed; they are colored red to indicate diploid Xi-only maps or green to indicate diploid Xa-only maps. The phased SNP calls used to generate homolog-specific maps are outlined in SI Appendix, Supplementary Materials and Methods. (B) A superloop forms between DXZ4 and FIRRE in human. Superloops are present at orthologous positions in rhesus macaque and mouse. In diploid Hi-C maps of mouse, the superloop is only seen on the Xi chromosome. (Resolution: 50 kb.)