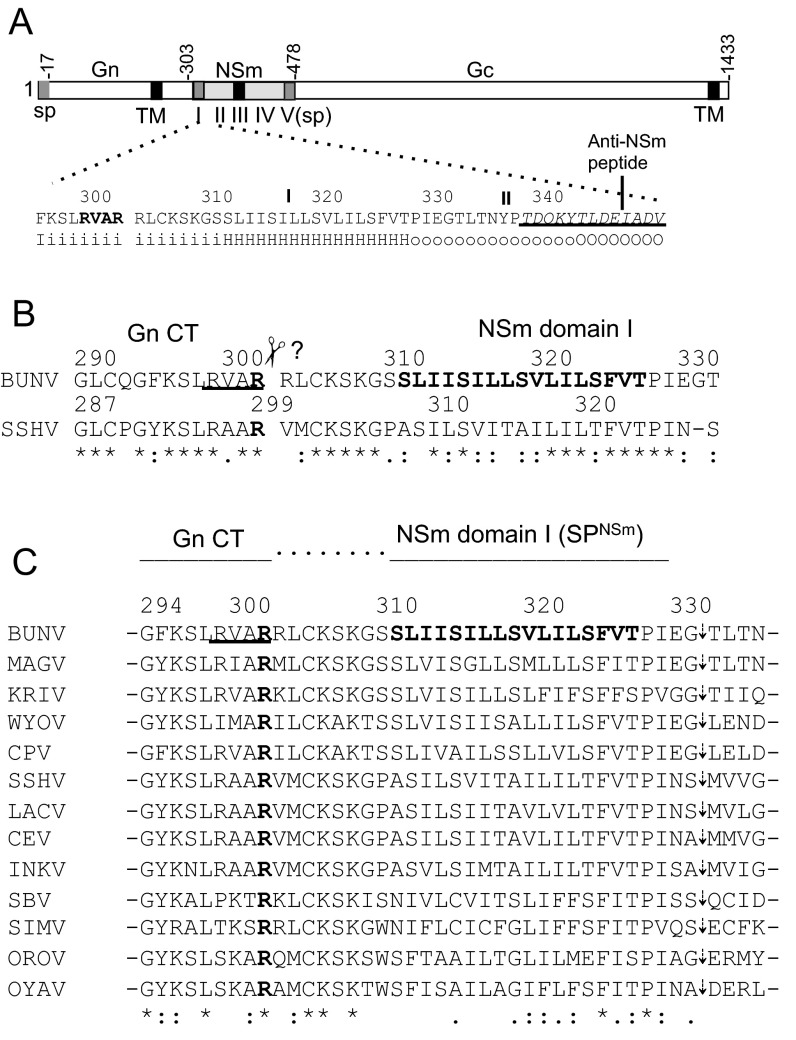
Fig. S1.
Schematic of BUNV GPC and mutations at RVAR motif and amino acid sequence alignment at the BUNV Gn-NSm junction. (A) BUNV GPC with positions of amino acid residues marking the predicted boundaries (Gn, NSm, and Gc) indicated. The amino acid sequence and the secondary structure prediction at the Gn–NSm junction (residues 295–350) are shown below. RVAR motif (residue 299–302) is in bold. The epitope to anti-NSm is underlined. The secondary structure is projected by using the HMMTOP server (www.enzim.hu/hmmtop) with H indicating hydrophobic transmembrane helix, i residue on inside, and O residues outside of transmembrane domains (TM/TMD). The NSm domains (I–V) (8) are shown under the NSm coding region. SP and TM are shown as gray and black boxes, respectively. (B) Alignment between BUNV and SSHV GPCs. The previously predicted last C-terminal residues are arginine (R) at residue 302 for BUNV and residue 299 for SSHV (in bold). (C) Amino acid sequence alignment of 13 orthobunyavirus GPCs (aligned to residues 294–335 of BUNV GPC). The alignment was created by using EMBL-EBI Clustal Omega program (www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo). The conserved arginine residues at residue 302 (for BUNV) are in bold. The GenBank accession numbers of orthobunyavirus GPCs used in alignment are as follows: BUNV (P04505), Maguari virus (MAGV; AAQ23639), Kairi virus (KRIV; ACV89517), Wyeomyia virus (WYOV; AGA54137), Cachoeira Porteira virus (CPV; AEZ35284), SSHV (ABX47014), La Crosse virus (LACV; AAB62804), California encephalitis virus (CEV; AAD53039), Inkoo virus (INKV; AAB93841), Schmallenberg virus (SBV; AGC93514), Douglas virus (DOUV; HE795091), Simbu virus (SIMV; YP_006590085), OROV (AGH07923), and Oya virus (OYAV; AGS56983).