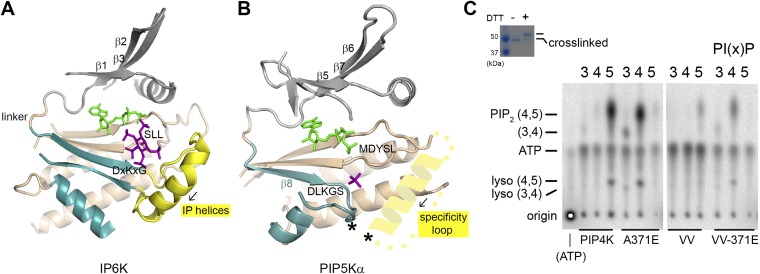
Fig. S7.
The specificity loop. (A) Structure of inositol hexakisphosphate kinase EhIP6KA in complex with ATP (green) and inositol(1,3,4,5,6)pentakisphosphate (purple) (PDB ID code 4O4E). Parts of the protein were omitted for clarity. The N- and C-lobes are colored gray and tan, respectively. Structural elements corresponding to the PIPB domain of PIPKs are colored blue. The IP helices are highlighted in yellow. (B) Structure of the zebrafish PIP5Kα with a schematic of the specificity loop capping the active site from the side of the membrane. The predicted helical segment within the specificity loop has the same directionality as the IP helices (black arrow). The asterisks indicate the engineered cross-linking sites in the VV mutant of PIP4Kα. (C) Substrate specificity of the cross-linked PIP4Kα VV mutant (V217C/V377C). The inserted gel confirms the complete cross-linking of the VV mutant used in the assay. Assay of wild-type PIP4Kα, A371E, VV, and VV-A371E with PI(3)P, PI(4)P, and PI(5)P as substrates. Given the lower in vitro catalytic efficiency of PIP4Kα compared with PIP5Kα, unused radioactive ATP migrates below the PI(3,4)P2 spot.