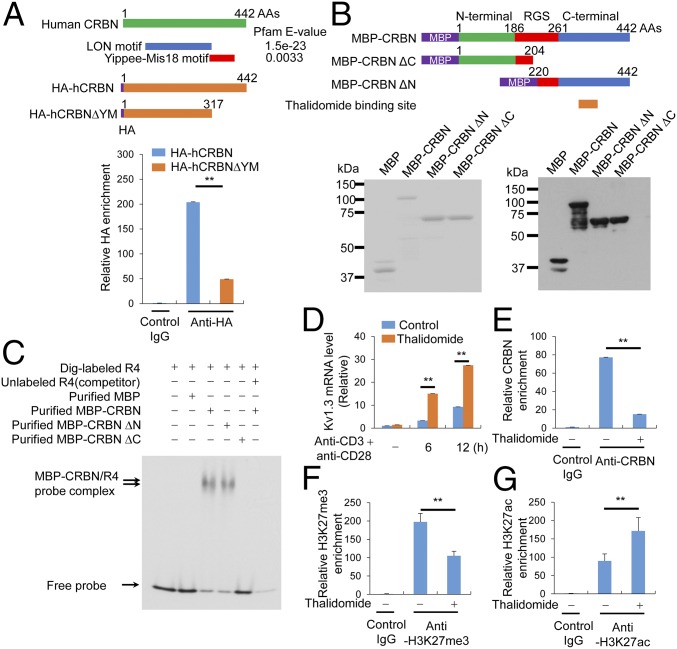
Fig. 4.
The C-terminal domain of CRBN is crucial for CRBN enrichment in Kcna3 chromatin. (A) The DNA-binding motif in CRBN was analyzed using a Pfam domain library (Upper), and HA-tagged CRBN enrichment on Kcna3 chromatin in Jurkat T cells was examined by ChIP (Lower). (B) MBP-CRBN proteins [i.e., full-length, C-terminal region-deleted (amino acids 1–204), and N-terminal region-deleted (amino acids 220–442) CRBN proteins] were expressed in E. coli and purified with MBPTrap HP (GE Healthcare Life Sciences). The purified proteins were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and Coomassie blue staining (Left) or immunoblot analysis (Right) with an anti-MBP monoclonal antibody (New England Biolabs). (C) EMSA was performed with the purified MBP-CRBN proteins and a Dig-labeled R4 DNA fragment. Analysis was performed using DIG Gel Shift Kit, 2nd generation (Roche). Unlabeled competition demonstrated that the EMSA probes specifically bound to the MBP-CRBN proteins. (D) Kv1.3 levels in CD4+ T cells activated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies were examined by quantitative RT-PCR. Before activation, CD4+ T cells were pretreated with 40 μM thalidomide for 6 h. (E) Relative levels of CRBN enrichment on Kcna3 chromatin from cells treated with or without thalidomide (40 μM) for 6 h were examined in ChIP assays incorporating anti-CRBN antibodies. (F and G) Relative levels of histone modification on Kcna3 chromatin in CD4+ T cells were examined in ChIP assays using anti-H3K27me3 (F) and anti-H3K27ac (G) antibodies after treatment with or without thalidomide for 6 h. Data are representative of two (A and B) or four (C–G) independent experiments. Results are expressed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test.