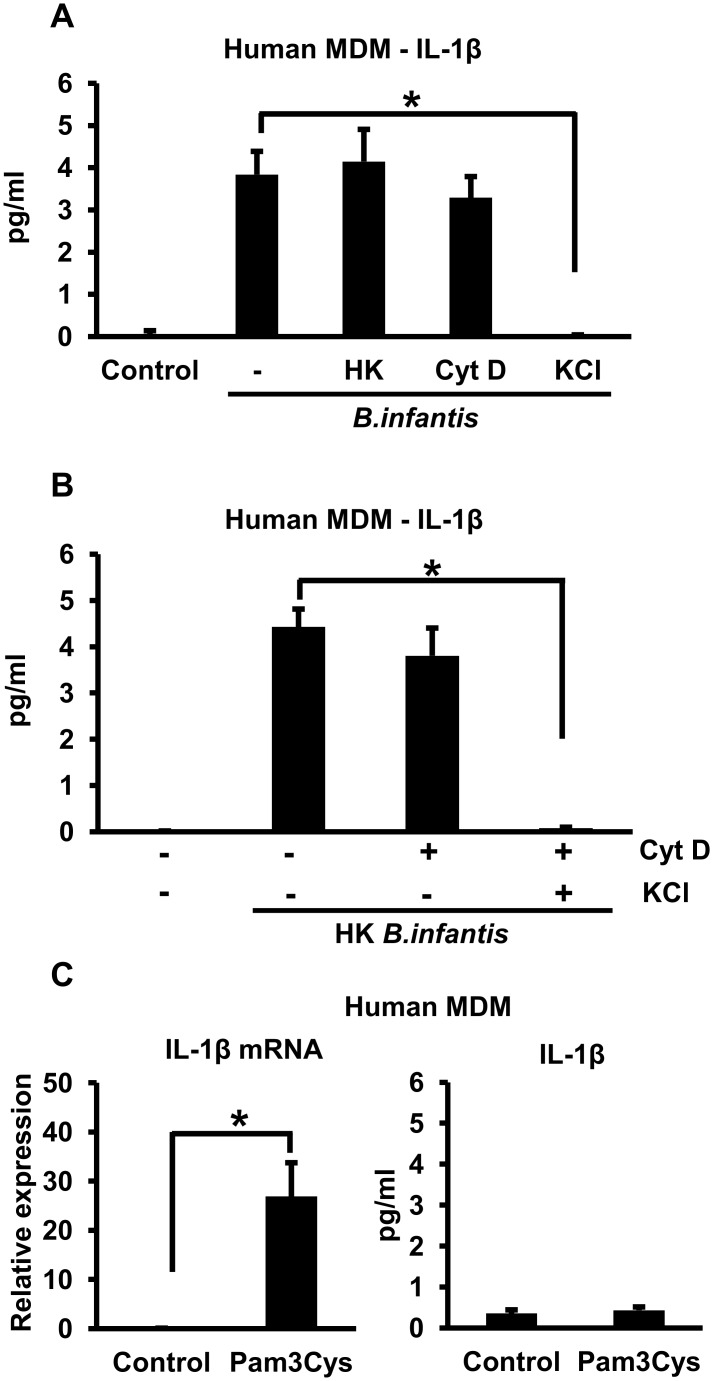
Fig 6. B. infantis-induced IL-1ß secretion by primary human MDMs.
A. Primary human MDMs were infected with equivalent numbers of live or heat-killed (HK) B. infantis for 1 hour in the presence or absence 5 μM cytochalasin D (Cyt D) or 50 mM potassium chloride (KCl) as indicated. The cells were washed, then incubated in fresh medium, with potassium chloride added back as appropriate. Supernatants were collected after 4 hours and IL-1ß concentrations determined by ELISA. *p < 0.0001, n = 6 per experimental condition. B. Primary human MDMs were infected with heat-killed B. infantis for 1 hour in the presence or absence 5 μM cytochalasin D (Cyt D) or 50 mM potassium chloride (KCl) as indicated. The cells were washed, then incubated in fresh medium, with potassium chloride added back as appropriate. Supernatants were collected after 4 hours and IL-1ß concentrations determined by ELISA. *p < 0.0001, n = 6 per experimental condition. C. Primary human MDMs were treated with 10 μg/ml of Pam3Cys for 4 hours, after which cellular RNA was analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR to determine IL-1ß mRNA levels (left panel) and supernatants were analyzed by ELISA to determine secreted IL-1ß concentrations (right panel). *p = 0.0002, n = 6 per experimental condition.