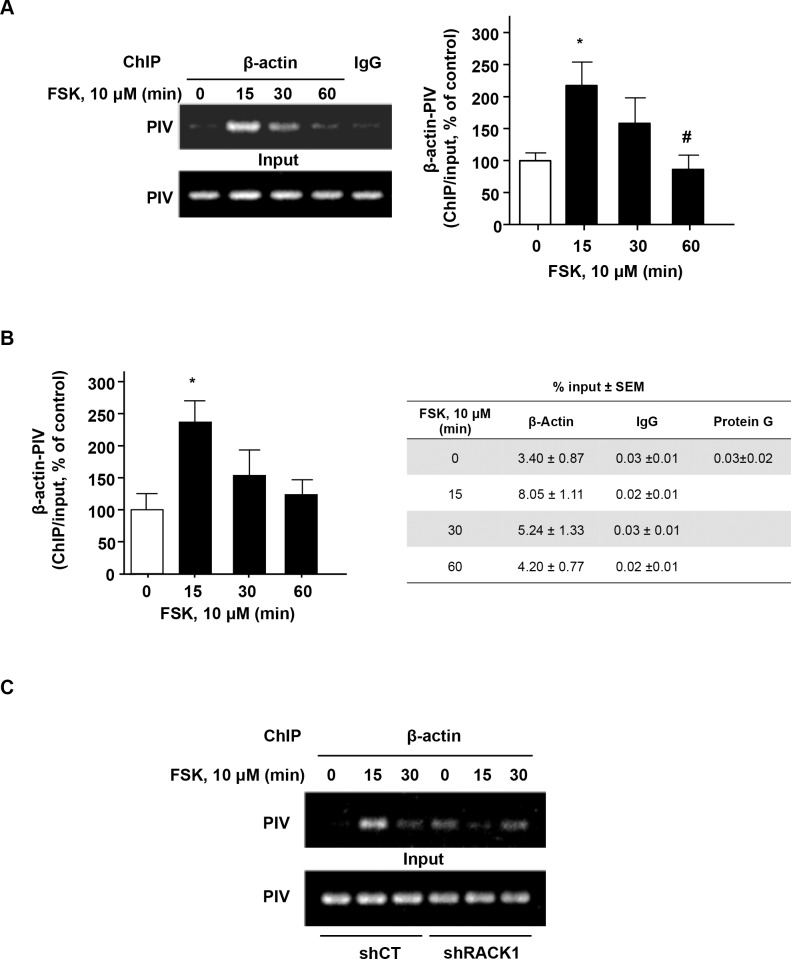
Fig 6. Activation of the cAMP pathway increases the association of β-actin with BDNF promoter IV via RACK1.
SH-SY5Y cells were treated with vehicle or with 10 μm FSK for the indicated time points, then lysed for a ChIP assay with normal IgG or anti- β-actin antibody. The β-actin-associated BDNF promoter IV (PIV) in the ChIP samples was detected by semi quantitative PCR (A) and quantitative PCR (B). A The level of PIV in the input was analyzed in parallel. The histogram depicts the mean ratio of β-actin -associated PIV to input PIV expressed as percent control ± SEM. One-way ANOVA detected a significant effect of the treatment [P = 0.020]. *p<0.05 (0 min vs. 15 min) and #p<0.05 (15 min vs. 60 min), Newman-Keuls post-hoc analysis. B The table depicts the quantity of BDNF PIV in the β-actin, IgG control or Protein G ChIP samples, expressed as percent of input ± SEM. One-way ANOVA detected a significant effect of the treatment [P = 0.041]. *p<0.05 (0 min vs. 15 min), Newman-Keuls post-hoc analysis. C SH-SY5Y cells were infected with control adenovirus (shCT) or adenovirus expressing shRACK1 for 3 days before treatment with 10 μM FSK for the indicated time points. A ChIP assay was then conducted as described in A. A n = 6, B n = 4 and C n = 2 per group.