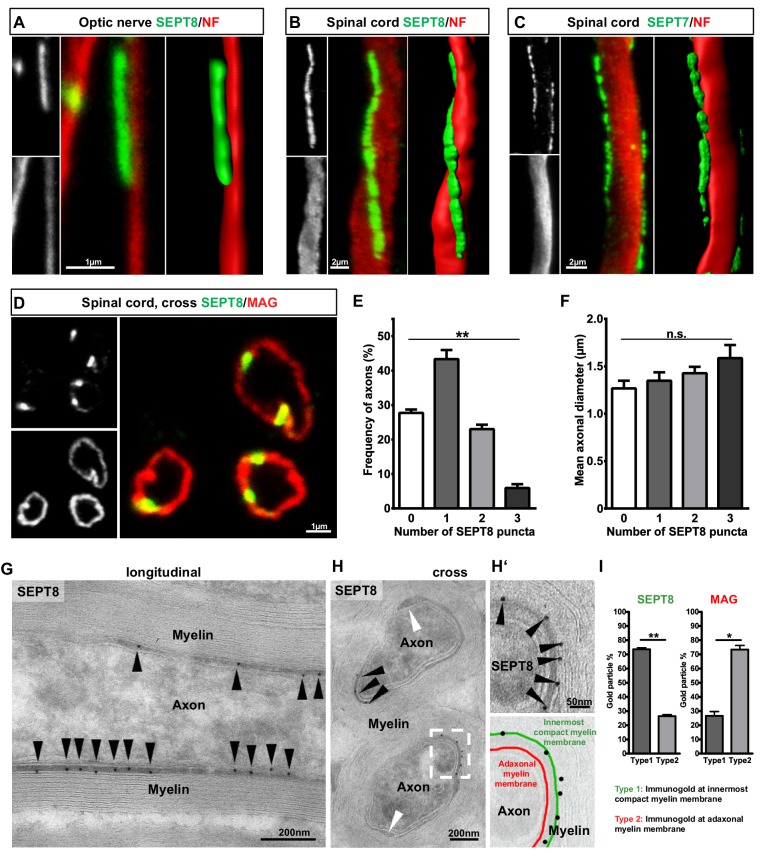
Figure 2. Septins form longitudinal filaments in the adaxonal compartment of mature CNS myelin.
(A–C) Immunofluorescent signal of SEPT8 and SEPT7 (green) extends longitudinally alongside axons identified by neurofilament-labelling (red). All panels show maximal projections of confocal stacks, and 3-dimensional reconstructions of longitudinally sectioned WT optic nerve (A) or spinal cord (B,C) at age P75. Images are representative of three animals. (D–F) SEPT8 (green) immunolabelling indicates that septin filaments localize to the adaxonal non-compact myelin compartment marked by MAG-immunolabelling (red) (confocal micrograph, D). The number of filaments represented by SEPT8-puncta is plotted in relation to their frequency per axon/myelin-unit (E) and the axonal diameter (F). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Analysis of 4 animals; repeated-measures-ANOVA; **p=0.0014 (E), n.s., p=0.26 (F). (G,H) Immunogold-labelling of cryosections identifies the localization of SEPT8 in the adaxonal myelin compartment in longitudinally (G) and cross-sectioned (H) optic nerves. Black arrowheads point at immunogold; white arrowhead points at the inner mesaxon. Images are representative of three animals. (H‘) Enlargement of the boxed area in H shows immunogold labelling of SEPT8 associated with the innermost membrane layer of compact myelin (green false colour in the overlay), not with the adaxonal myelin membrane (red false colour in the overlay). (I) Quantification of immunogold labelling of SEPT8 and MAG relative to the innermost membrane layer of compact myelin (type 1) and the adaxonal myelin membrane (type 2). Note that SEPT8 immunogold labelling is associated with the innermost membrane layer of compact myelin while MAG labelling is associated with the adaxonal myelin membrane. Mean ± SEM. Analysis of 3 animals; two-tailed paired t-test; SEPT8 **p=0.002, MAG, *p=0.02.