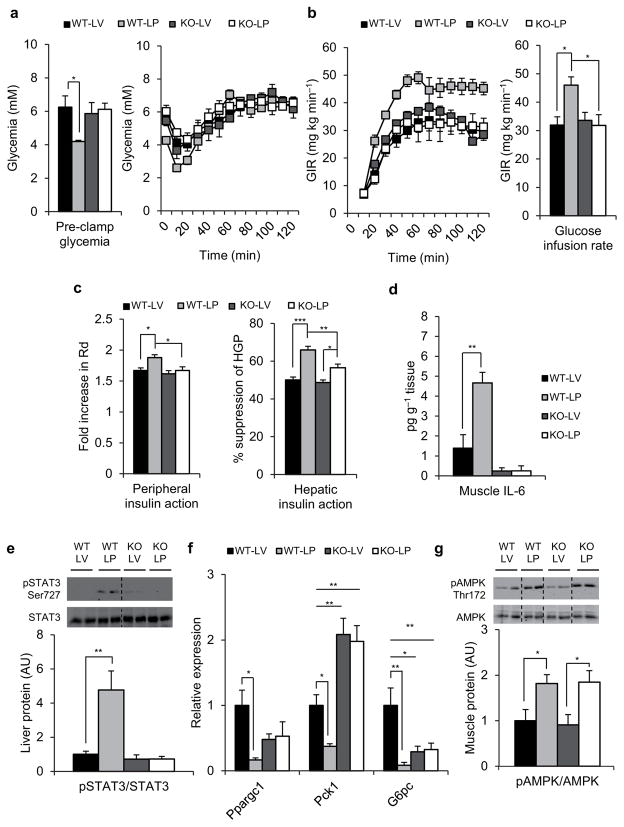
Figure 3.
IL-6 is required for the insulin sensitizing actions of PDX. (a) Pre-clamp glycemia (left) and clamp glucose excursion (right), (b) glucose infusion rate (GIR) (left) and mean GIR for the final 60 min of clamp (right) in wild-type (WT) or IL-6 null (KO) lipid-infused (L) PDX (P) or vehicle (V) treated animals. (c) Peripheral insulin action expressed as fold increase in Rd during the clamp (left) and hepatic insulin action expressed as percent suppression of hepatic glucose production (HGP; right), (d) Skeletal muscle IL-6 content (e) Immunoblots for pSTAT3 Ser727 and total STAT3 and (f) relative mRNA expression of Ppargc1, Pck1 and G6Pc normalized to GAPDH in liver from clamped wild-type (WT) or IL-6 null (KO) lipid-infused (L) PDX (P) or vehicle (V) treated animals. (g) Immunoblots for pAMPK Thr172 and total AMPK in gastrocnemius muscle from clamped wild-type (WT) or IL-6 null (KO) lipid-infused (L) PDX (P) or vehicle (V) treated animals. Quantification of densitometry analyses for immunoblots is shown below the representative gels. Dotted lines indicate that lanes were run on the same gel but were noncontiguous. WT-LV, wild-type lipid-infused vehicle, n = 6 mice. WT-LP, wild-type lipid-infused PDX, n = 5 mice. KO-LV, IL-6 null lipid-infused vehicle, n = 5 mice. KO-LP, IL-6 null lipid-infused PDX, n=6 mice. Data are mean ± s.e.m, * P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 calculated using analysis of variance.