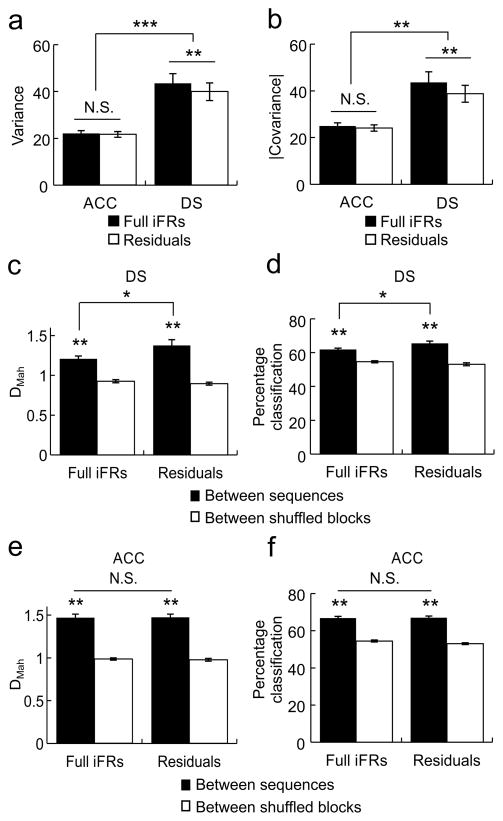
Figure 5.
Consistency of sequence encoding in the ACC and DS within behavioral epochs. a) Ensemble variance calculated based on activities during the time bins within each pair of common-segment lever presses was higher in the DS than in the ACC. Ensemble variance calculated on the residual iFR matrices (right, white) was smaller than the variance calculated from full iFR matrices (right, black) in the DS, but the two were equivalent in the ACC (left bars). b) Ensemble covariance was also greater in the DS (right) than in the ACC (left). Ensemble covariance calculated on the residual iFR matrices (white) was smaller than the covariance calculated from full iFR matrices (black) in the DS, but the two were equivalent in the ACC. c) In ACC ensembles, between-sequence DMah calculated using the residuals from the initial behavioral regression was equivalent to that calculated using the full iFRs, and both were greater than shuffled controls. d) In ACC ensembles, between-sequence leave-one-out MDA using the residual iFR matrices (right) was equivalent to that calculated using the full iFR matrices (left). e) In contrast to the ACC, in DS ensembles, DMah calculated using the residual iFR matrices from the initial behavioral regression (right) was greater than that calculated using the full iFR matrices (left), although both the full iFRs and the residuals still contained robust sequence information. f) In DS ensembles, sequence classification using the residual iFR matrices (right) was more accurate than when calculated using the full iFR matrices (left). Error bars indicate s.e.m. *p<0.05, ** p<0.001, *** p<0.00001