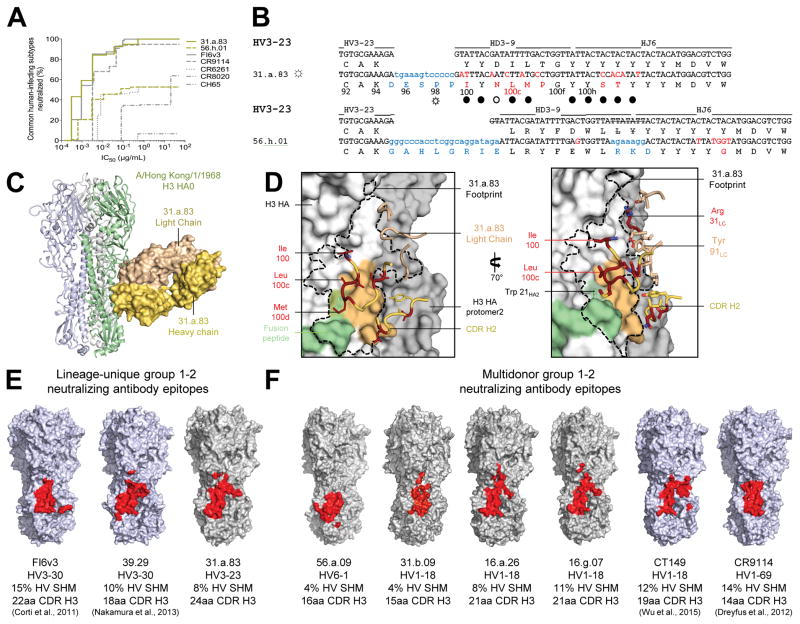
Figure 5. A conserved site of group 1 and 2-influenza A virus vulnerability targeted by multidonor and lineage-unique antibodies.
(A) Neutralization breadth-potency curve for HV3-23-derived antibodies, on a panel of influenza A viruses that includes subtypes known to infect humans. (B) Immunoglobulin heavy chains utilizing germline genes HV3-23, HD3-9 and HJ6, with sequences annotated as described in Figure 2A. (C) Co-crystal structure of Fab 31.a.83 in complex with HA (H3-HK68). (D) Epitope for antibody 31.a.83 (outlined in black) with heavy chain depicted in yellow and junction-encoded residues (highlighted in blue), mutated residues (in red), and germline-encoded residues (in gold) and with light chain depicted in tan. (E–F) Antibodies capable of neutralizing group 1 and 2 influenza A viruses recognize overlapping epitopes within the HA stem (colored red). The HA surface is colored blue for structures determined previously (FI6v3 PDB ID:3ZTN; 39.29 PDB ID:4KVN; CT149 PDB ID:4R8W; CR9114 PDB ID:4FQI), and gray for structures determined in the current study. See also Figures S3–S6 and Tables S3–S7.