Figure 4.
High-Confidence EJC Binding Sites Reveal that BTZ Is an Essential EJC Component at the Canonical Deposition Site
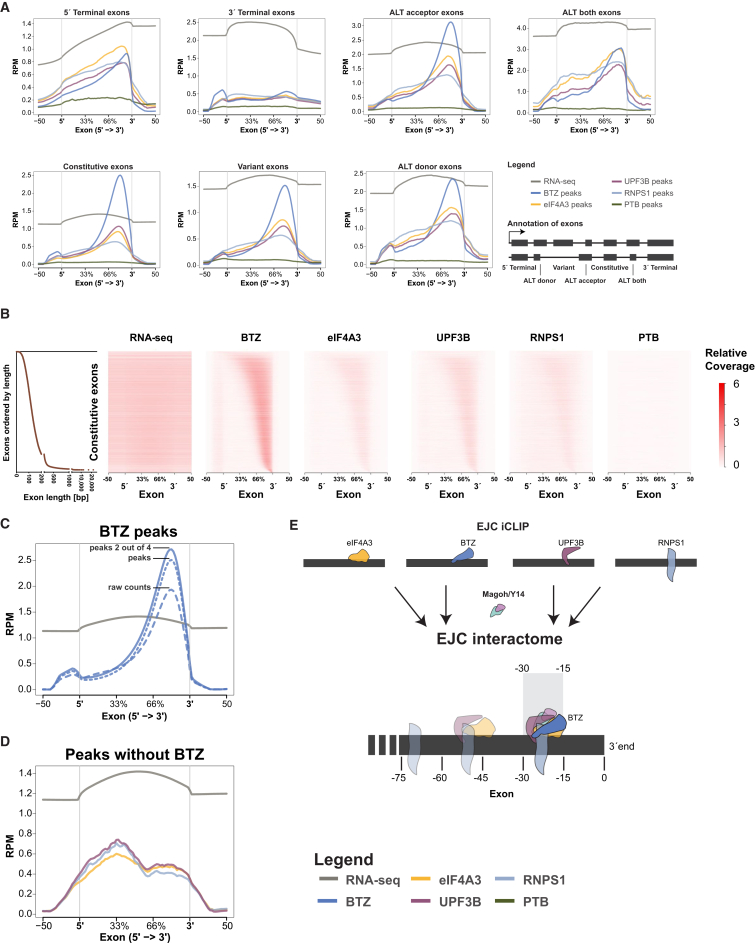
(A) Internal exons are predominantly bound by EJC components and constitutive exons display the strongest BTZ signal relative to their abundance. The average profile of reads covering exons are plotted for: (1) 5′ terminal exons; (2) 3′ terminal exons; (3) constitutive exons present in all isoforms; (4) variant exons not present in all isoforms; (5) exons with alternative acceptor sites (ALT acceptor); (6) exons with alternative donor sites (ALT donor); and (7) exons with both alternative donor and acceptor sites (ALT both) using ngsplot software (Shen et al., 2014).
(B) Histogram on the left hand side shows the length of the constitutive exons and is aligned to the heatmaps showing RNA-seq and iCLIP coverage across individual exons ordered by their length. The length of the exons can be extracted from the histogram. This image confirms that most exons harbor an EJC at the 3′ end and demonstrate that the EJC signal strength is independent of exon length. The color key represents the signal strengths of the RNA-seq and iCLIP data.
(C) Average coverage profiles across constitutive exons for BTZ iCLIP: (1) raw reads; (2) reads in peaks; and (3) reads in peaks that overlap with at least one of the other EJC proteins (eIF4A3, UPF3B, and RNPS1) are restricted to the 3′ end of exons. The peak detection and filtering approaches increased the BTZ signal.
(D) By contrast, the average exon profiles for eIF4A3, UPF3B, and RNPS1 iCLIP binding sites that were not determined concurrently by BTZ binding sites were absent of an EJC signal close to the 3′ end of exons suggesting that non-canonical binding sites do not contain the fully assembled EJC. The profiles are plotted as read CPM mapped reads (RPM).
(E) The integrated analyses over four distinct components of the EJC revealed that BTZ determines the position of fully assembled EJCs to the canonical deposition sites at 15–30 nt upstream of exon-exon junctions. Non-canonical depositions sites of EJC proteins (alone or in subcomplexes) located in other regions of the exon are less common and do not contain BTZ.
See also Figure S4 and Tables S4–S6.