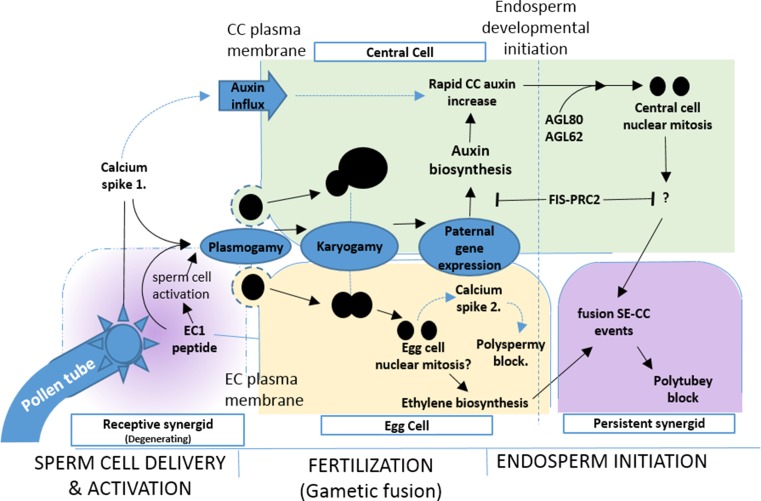
Fig. 2.
Diagram of signalling events of Arabidopsis fertilisation and endosperm initiation. Procession of the events and signalling involved in fertilization and endosperm developmental initiation in Arabidopsis. Pollen tube rupture in the degenerating synergid releases the sperm cells. Associated calcium signalling triggers the release of EC1 peptides involved in sperm cell activation and potentially auxin influx to the CC. Individual sperm cells fuse with E and CC (Plasmogamy) followed by fusion of their respective nuclei (Karyogamy). In the CC maternal auxin biosynthesis, genes are repressed by the FIS-PRC2. Nuclear fusion in the CC initiates paternal gene expression, which results in auxin biosynthesis and increase in the CC that may also include auxin influx. In conjunction with AGL62 activity, increased auxin concentration triggers the release of mitotic arrest mechanisms and nuclear proliferation in the CC. Nuclear fusion in the egg cell triggers calcium signalling associated with rapid polyspermy blockade along with ethylene biosynthesis responsible for triggering plasmogamy of the persistent synergid with the CC and polytubey blockade. Solid black arrows indicate reported signalling events. Blue-dotted arrows represent proposed signalling events