Figure 1.
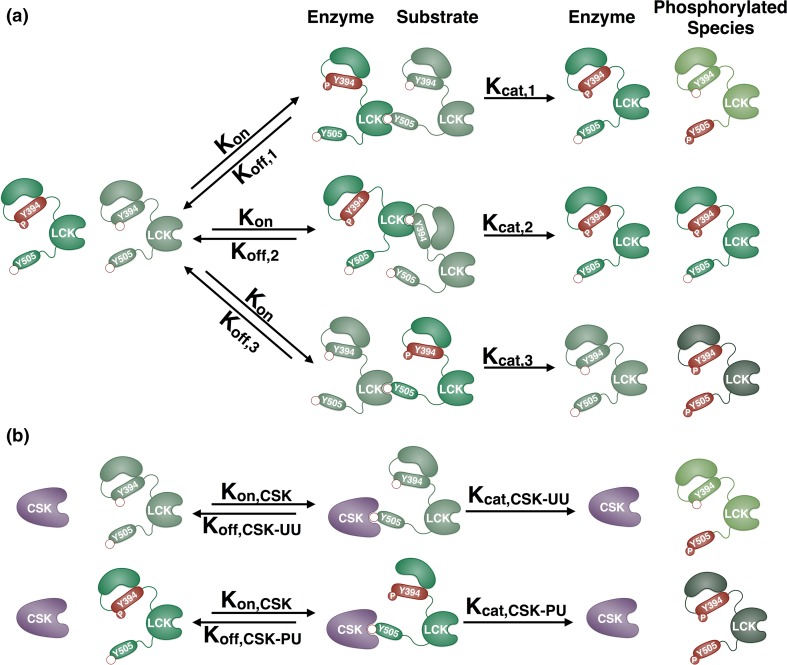
Schematic of LCK interactions. (a) The possible interactions between a representative pair of LCK species, U394U505 and P394U505, are illustrated. LCK can phosphorylate itself in trans when the catalytic domain of one molecule binds to a tyrosine phosphorylation site on another molecule. Phosphorylated tyrosine residues are red and have a filled red circle labeled with “P”, unphosphorylated sites are green and have an empty red circle. Each LCK species (U394U505, P394U505, U394P505, and P394P505) is represented by a different color molecule. All of the species can bind to a substrate site (Y394 or Y505) with a single rate of association (K on) and different dissociation rates (K off,1, K off,2, K off,3). The catalytic rates are also different depending on the enzyme and substrate pairs (denoted as K cat,1, K cat,2, K cat,3). (b) Diagram of all possible interactions of the enzyme CSK with LCK. CSK can phosphorylate LCK U394U505 or P394U505 on Y505. The pairs can bind with the same association rate (K on,CSK), but CSK-LCK pairs will dissociate (K off,CSK-UU, K off,CSK-PU) and phosphorylate (K cat,CSK-UU, K cat,CSK-PU) with different rates.