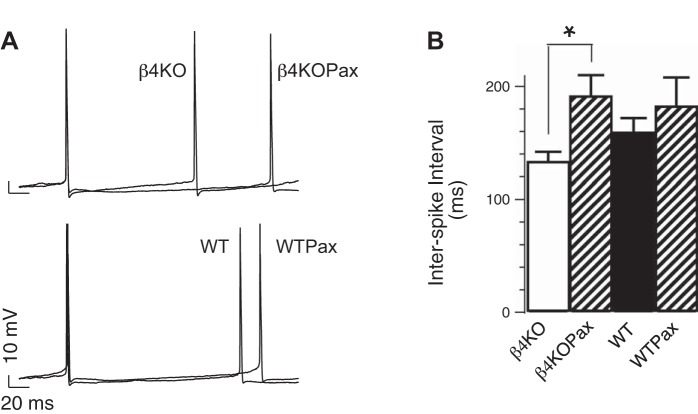
Fig. 1.
Effect of large-conductance calcium- and voltage-activated potassium (BK) channel blockers on dentate gyrus (DG) action potential (AP) firing. A: representative APs recorded from knockout (KO) β4−/− or wild-type (WT) DG neurons at threshold current injection. Traces represent APs in the absence or presence of 5 μM paxilline (Pax). X and Y scales represent 20 ms and 10 mV, respectively. B: averaged interspike interval (ISI; in ms, β4KO: 133 ± 9, n = 23, β4KOPax: 191 ± 19, n = 8; WT: 159 ± 13, n = 22, WTPax: 182 ± 26, n = 8). β4−/− and β4−/−Pax are significantly different (P = 0.006). Difference between WT and WTPax was not significant (P = 0.4). *P < 0.05.