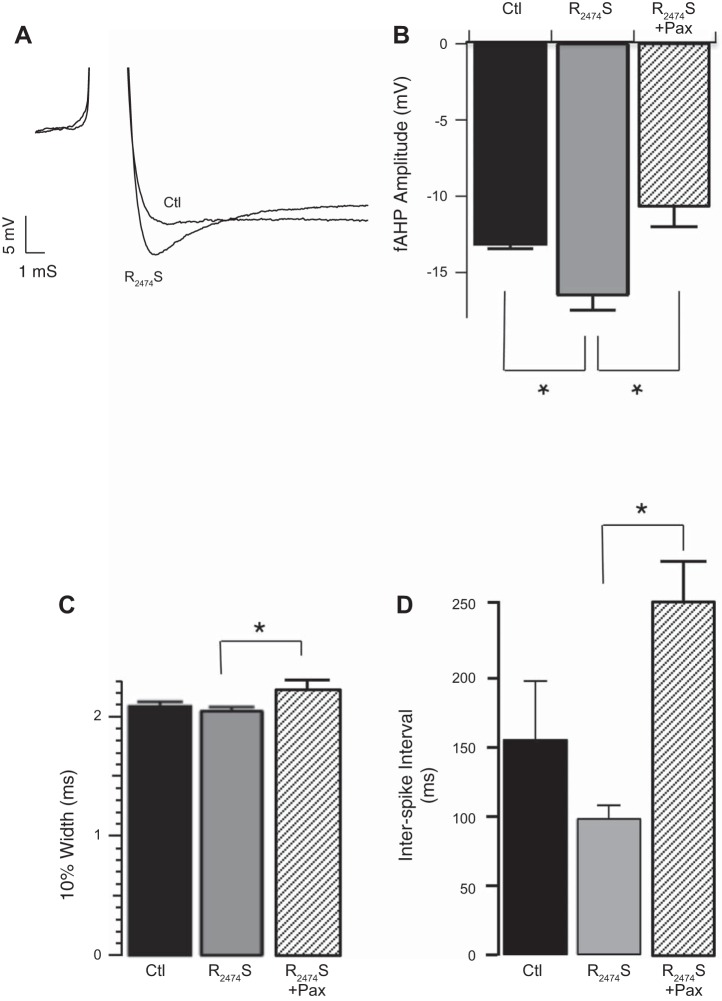
Fig. 7.
RyR2 gain-of-function mutation R2474S causes an increased fAHP amplitude. A: representative fAHP from R2474S and from control WT sibling dentate gyrus (DG) granule neuron. B and C: fAHP amplitude (control −13.1 ± 0.3; R2474S −16.5 ± 1.0; R2474S + Pax 10.6 ± 1.4, P = 0.004 for control vs. R2474S, P = 0.002 for R2474S vs. R2474S + Pax, n = 8, 9, and 6 respectively, B) and AP 10% width (control 2.0 ± 0.05; R2474S 2.0 ± 0.03; R2474S + Pax 2.2 ± 0.07, P = 0.92 for control vs. R2474S, P = 0.02 for R2474S vs. R2474S + Pax, n = 9, 13 and 6, respectively, C) at threshold current injections. D: ISI at threshold current injections (control 155 ± 43; R2474S 98 ± 10; R2474S + Pax 252 ± 29, P = 0.2 for control vs. R2474S, P = 0.0001 for R2474S vs. R2474S + Pax, n = 8, 8 and 6, respectively). Gray bars are R2474S mice, stippled bars are R2474S + Pax, and black bars are control littermates. *P < 0.05.