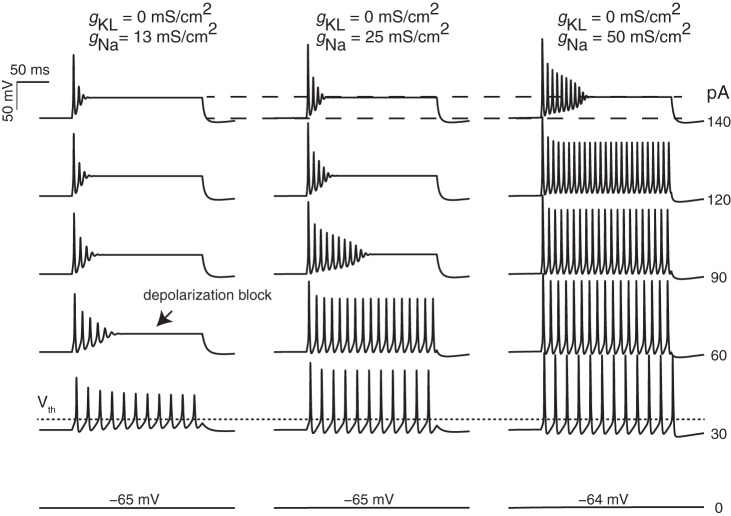
Fig. 5.
Influence of maximum gNa on firing pattern. Responses are shown for simulations with gKL fixed to 0 mS/cm2 and gNa varying (columns). Current-step amplitudes ranged from 0 to 140 pA. As sodium channel density increased, the size of the second and subsequent spikes became larger, the depth of the second and subsequent AHPs became larger, and the current step at which depolarization block occurs (arrow) was also larger. Resting potential (voltage at 0 pA injection), spike threshold (short-dashed line), and steady-state depolarization potential (between the 2 long-dashed lines) were not significantly influenced by the sodium current density. For the 3 columns, the average spike intervals at the 30-pA current steps are 18.1 ± 0.22, 18.1 ± 0.19, and 17.9 ± 0.17 ms, respectively.