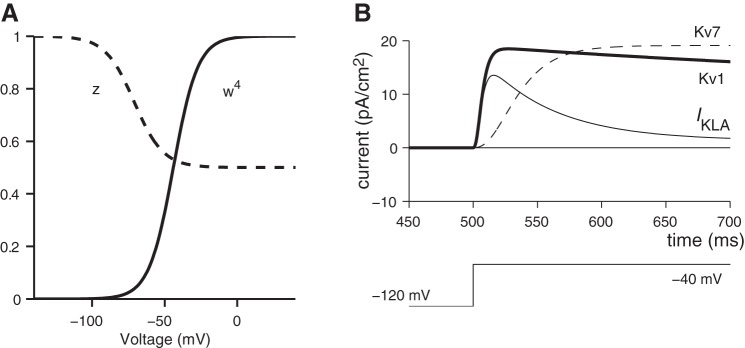
Fig. A1.
Voltage dependence and kinetics of IKL. A: voltage dependence of channel activation (w∞4; solid line) and inactivation (z∞; dashed line). B: IKL simulated for a voltage-clamp step that depolarizes the cell from an initial voltage of −140 mV (outside the activation range of IKL) to −45 mV (within the activation range for IKL). Simulations show 3 currents: the first is a Kv1-type current that activates fast and inactivates slowly but only partially (thick solid line), the second is a KCNQ-type current with slow activation and no inactivation (Kv7; dashed line), and the third is a transient current that activates fast and inactivates fast and completely (IKLA; thin solid line).