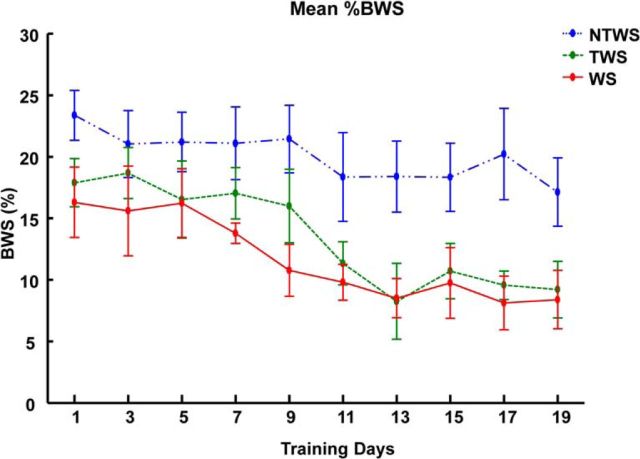
Figure 5.
Robotic rehabilitation training reduces %BWS provided by robotic assistance in the WS, TWS, and NTWS groups. Plot represents mean ± SE (%BWS) changes for each group over the course of robot rehabilitation training. There was a significant training effect (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA, F(9,135) = 10.73, p < 0.001) on reductions in %BWS over time in all three groups. There were also differences in the mean %BWS among the groups as indicated by the group effect reported in the two-way repeated-measures ANOVA (F(2,15) = 3.79, p = 0.047). *Significant difference between WS and NTWS groups (p < 0.05). #Significant difference between TWS and NTWS groups (p < 0.05).