Figure 3.
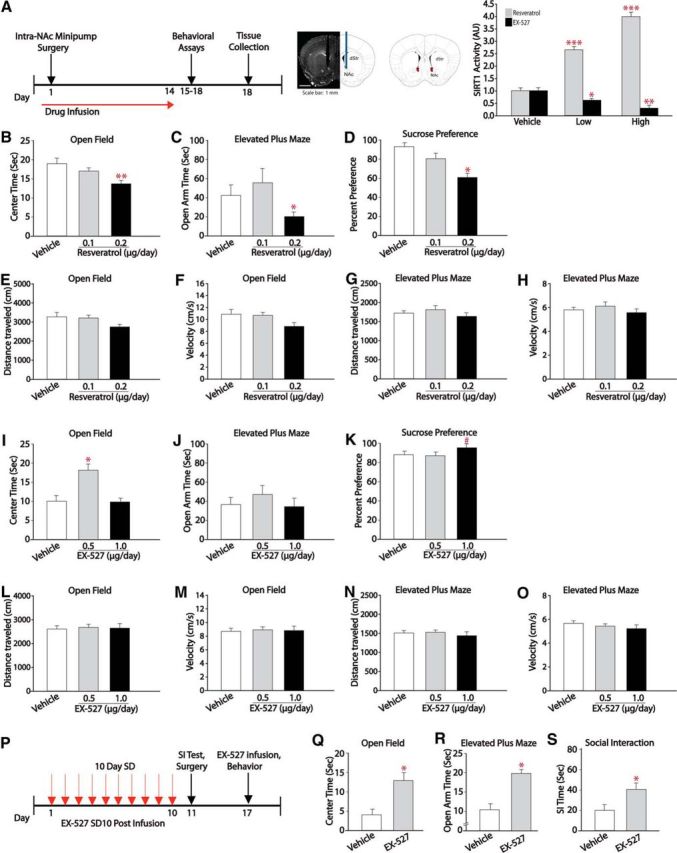
Pharmacological modulation of SIRT1 activity in the NAc regulates anxiety and depression-like behavior bidirectionally. A, Schematic of experimental design. Mice were implanted with osmotic minipumps filled with resveratrol (0.1 μg/d or 0.2 μg/d) or the SIRT1 antagonist EX-527 (0.5 μg/d or 1.0 μg/d) targeting the NAc for 14 d and tested on a battery of behavioral tasks on days 15–18, followed by tissue collection. SIRT1 catalytic assay shows increased SIRT1 deacetylase activity in the NAc of mice infused with resveratrol (n = 7) and decreased SIRT1 deacetylase activity in the NAc of mice infused with EX-527 (n = 6). B–H, Sustained intra-NAc infusion of resveratrol at 0.2 μg/d results in decreased time in the center of an open field (n = 8–9; B), decreases time in the open arms of an elevated-plus maze (n = 6–10; C), and decreased sucrose preference (n = 6–7; D) without changes in exploratory behaviors (E–H). I–O, Sustained intra-NAc infusion of EX-527 at 0.5 μg/d results in increased center time on an open field (n = 13; I) and no changes in exploratory behaviors (L–O). P–S, Effects of EX-527 infusions on the development of stress-induced depression- and anxiety-like behaviors. EX-527 infusions block stress induced depression- and anxiety-like symptoms as reflected by increased social interaction time (n = 6–7; S) and increased time in the center of an open field (n = 7; Q) and open arms of an elevated-plus maze (n = 6–8; R). #p < 0.09, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM.
