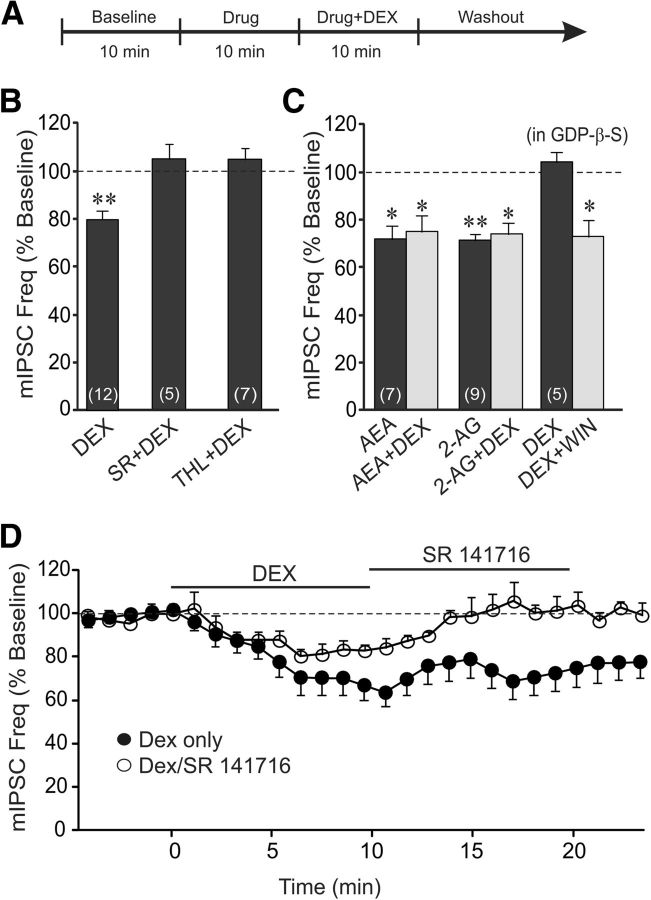
Figure 3.
The rapid glucocorticoid suppression of synaptic inhibition is mediated by activation of the release of a retrograde endocannabinoid messenger. A, Timeline of the experimental paradigm that produced the data shown in B and C. B, The CB1 receptor antagonist SR and the inhibitor of 2-AG synthesis THL blocked the DEX-induced decrease in mIPSC frequency. C, The endocannabinoids 2-AG and AEA mimicked (AEA and 2-AG) and occluded (AEA+DEX and 2-AG+DEX) the rapid DEX-induced suppression of mIPSC frequency. Blocking postsynaptic G-protein activity with intracellular GDP-β-S application blocked the postsynaptic DEX-induced decrease in mIPSC frequency (DEX), but not that caused by presynaptic CB1 receptor activation with bath application of WIN55,212-2 (DEX+WIN). D, Time course of the mean relative changes in mIPSC frequency elicited by a single 10 min application of DEX (filled circles), and by a 10 min application of DEX followed by a 10 min application of the CB1 receptor antagonist SR (open circles). Blocking CB1 receptors reversed the glucocorticoid-induced suppression of mIPSC frequency. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.