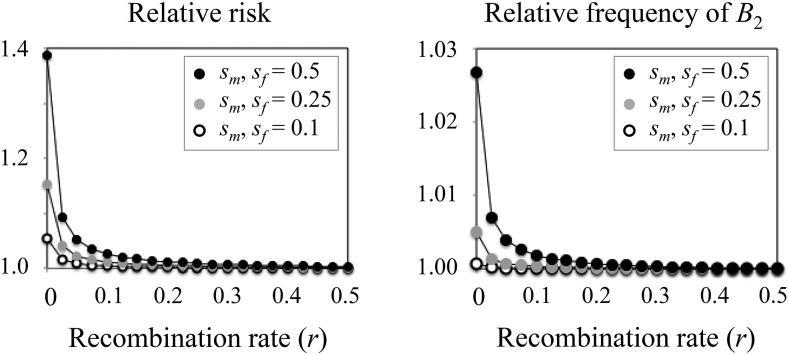
Figure 4.
Mutation accumulation under diploid selection and arbitrary linkage between loci. The left panel shows the relative risk of a deleterious mutation on haplotypes that carry a male-beneficial vs. a female-beneficial sexually antagonistic allele (as in Figure 3). The right panel displays the equilibrium frequency of a deleterious allele relative to its expected frequency in the absence of sexually antagonistic selection at the A locus (as in Figure 1). Results are based on deterministic forward simulations, using recursions from the Appendix. Both panels show the accumulation of a partially recessive (h = 0.2) deleterious mutation with female-limited effect (tm = 0; tf = 0.1), and under sexually symmetric mutation (uf = um = 10−5). The sexually antagonistic locus evolves under balancing selection with additive and symmetrical fitness effects between the sexes (sm = sf = 0.1, 0.25 or 0.5; km = kf = 1/2 within Table 1).