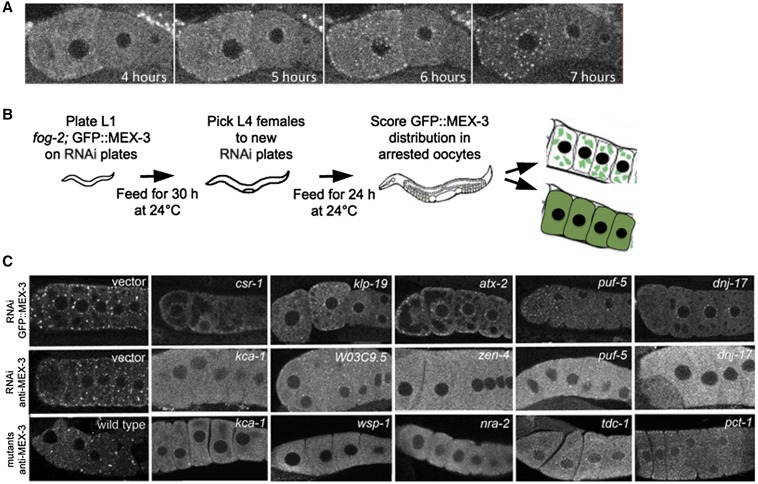
Figure 1.
RNAi screen identifies positive regulators of RNP granule assembly in arrested oocytes. (A) Live imaging of fog-2;GFP::MEX-3 unmated female shows rapid assembly of GFP::MEX-3 granules begins soon after the L4 stage of development. By 7 hr post-L4, granules are prominent and enriched near the cortex and nuclear membrane, and the level of cytosolic GFP is decreased relative to 4 hr post-L4. (B) Cartoon of feeding RNAi screen. 1536 genes were screened and 319 genes were identified. (C) Representative images showing disruption of RNP granule assembly after knockdown of gene expression. Top row: GFP::MEX-3 distribution after RNAi in fog-2 background. The negative control was RNAi using an empty vector (left), and GFP::MEX-3 granules are prominent. RNP granules are disrupted, and levels of diffuse GFP::MEX-3 are increased after knockdown of five positive hits. Middle row: Anti-MEX-3 staining after RNAi in fog-2 worms reveals similar large granules in negative control (left) and similar disruption of endogenous RNP granules. Bottom row: Anti-MEX-3 staining in arrested oocytes of wild-type (left) and in mutants depleted of sperm validates the GFP::MEX-3 reporter results. GFP, Green fluorescent protein; RNAi, RNA interference; RNP, ribonucleoprotein.