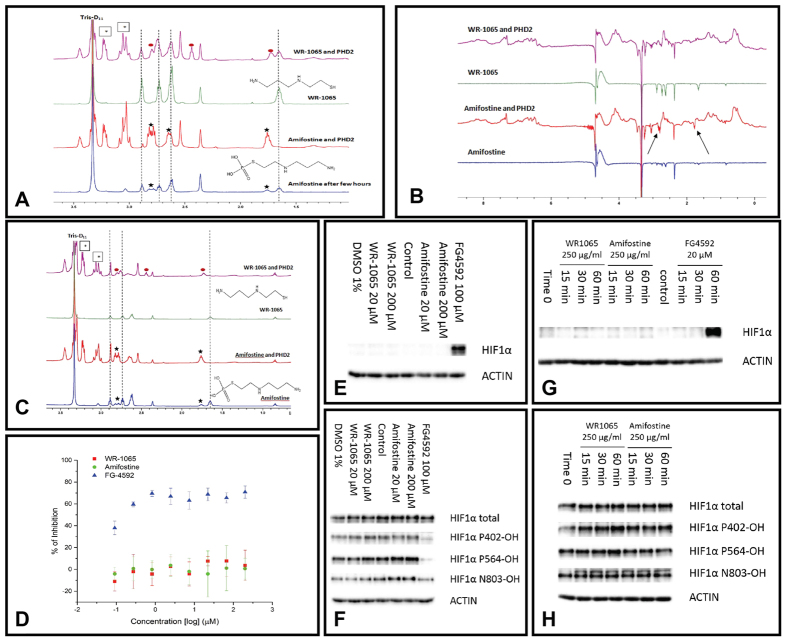
Figure 4.
(A) Single-concentration qualitative binding screening by 1H NMR. Assay: 500 μM of compound (amifostine/WR-1065), 200 μM Zn(II), 50 μM apo-PHD2, where necessary, buffered with 50 mM Tris-D11 (pH 7.5), 0.02% NaN3 in 90% H2O/10% D2O. Peaks for amifostine: black stars, dephosphorylated amifostine/WR-1065: dashed lines, disulfide WR-1065 (WR-33278): red circles, protein sample peaks (e.g. glycerol): boxed stars. Amifostine reacts giving thiol WR-1065. No evidence for phosphorylated amifostine binding to PHD2 is apparent. Line broadening of WR-1065 peaks, characteristic of weak binding. (B) Screening by wLOGSY NMR. Assay: 500 μM amifostine or WR-1065, 200 μM Zn(II), 50 μM apo-PHD2, if needed buffered as above in 90% H2O/10% D2O. Results imply that amifostine doesn’t bind to PHD2 (compound peaks are highlighted by arrows) within detection limits; WR-1065 shows evidence of weak binding. (C) 1H CPMG NMR screening of equimolar mixtures. Assay: 100 μM amifostine/WR-1065, 200 μM Zn(II), 100 μM apo-PHD2; if needed buffered as above in 90% H2O /10% D2O. For WR-1065 partial reduction in peak intensity is observed, characteristic of weak binding, with the appearance of a new species, WR-33278. (D) Inhibition of the PHD2 catalytic domain of PHD2 (residues 181–426), assayed by AlphaScreen method, shows no evidence of inhibition by amifostine/WR-1065 (to 200 μM). FG-4592 is a positive control. Conditions: 5 nM PHD2181–426, 20 mM Fe(II), 200 mM ascorbate, 2 mM 2OG, 60 nM HIF1α-CODD peptide (residue 554–574), and inhibitor DMSO (2% DMSO final concentration). Inhibitors were pre-incubated with PHD2 (15 mins) before incubation (10 mins). (E) Immunoblotting amifostine/WR-1065 (6 hours, Hep3b cells) treatment. (F) Immunoblotting after amifostine/WR-1065 (6 hours, RCC4 cells) treatment. (G) Immunoblotting after amifostine/WR-1065 (15/30/60 mins) treatment. (H) Immunoblotting of prolyl-hydroxylated HIF1α after amifostine/WR-1065 (15/30/60 mins) treatment.