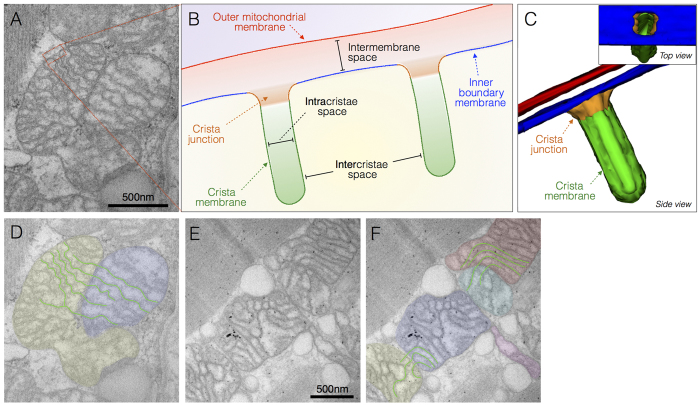
Figure 1. Normal mitochondrial ultrastructure.
(A) Transmission electron micrograph of normal mitochondria in human skeletal muscle showing typical tubular cristae, and crista junctions. (B) Schematic representation of crista junctions, associated structures, and parameters measured in this study. (C) Three-dimensional schematic of normal tubular cristae structure. The outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM, red), and three functionally distinct regions of the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM): inner boundary membrane (blue), crista junction (orange), and crista membrane (green). (D) Same image as in A with pseudocolored adjacent but distinct mitochondria and outlined crisate membranes undergoing trans-mitochondrial cristae coordination (see ref. 34 and text for discussion). (E) Unprocessed and (F) pseudocolored transmission electron micrographs of normal human skeletal muscle illustrating mitochondria with normal shapes and sizes, with electron-dense curvilinear cristae, with some exhibiting trans-mitochondrial cristae coordination.