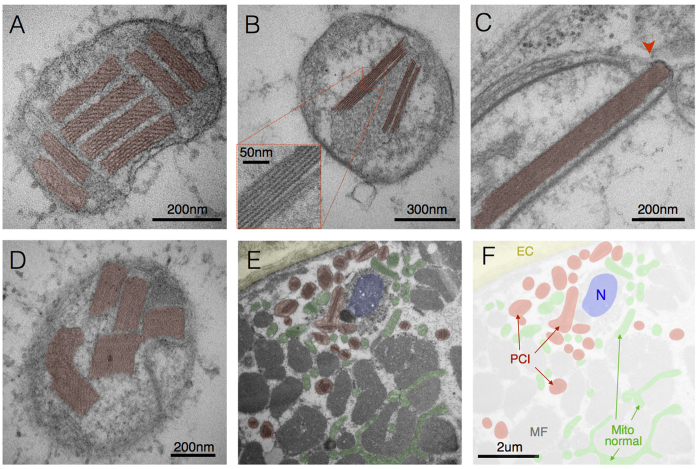
Figure 2. Paracrystalline inclusions (PCIs).
(A) Type I PCIs occupying most of a mitochondrion’s volume in skeletal muscle with a single mtDNA deletion (patient 1). (B) Linear Type I PCI in mitochondrion from a case of m.8344A>G (patient 5). (C) Disruption of IMM and OMM (arrowhead) by a rigid type II PCI, and (D) other examples of type II PCIs from a case of m.8344A>G (patient 4). (E) Subsarcolemmal region of a muscle fiber showing the extracellular space (EC, yellow) and sarcolemma, profile of a nucleus (N, blue), myofibrils (MF), mitochondria with PCI (red) and normal mitochondria (green), with (F) pseudocolored mask (patient 1). Note the greater abundance of PCI-containing mitochondria in the perinuclear SS compartment compared to the intermyofibrillar compartment, consistent with the distinctive requirement for de novo protein synthesis for PCI formation.