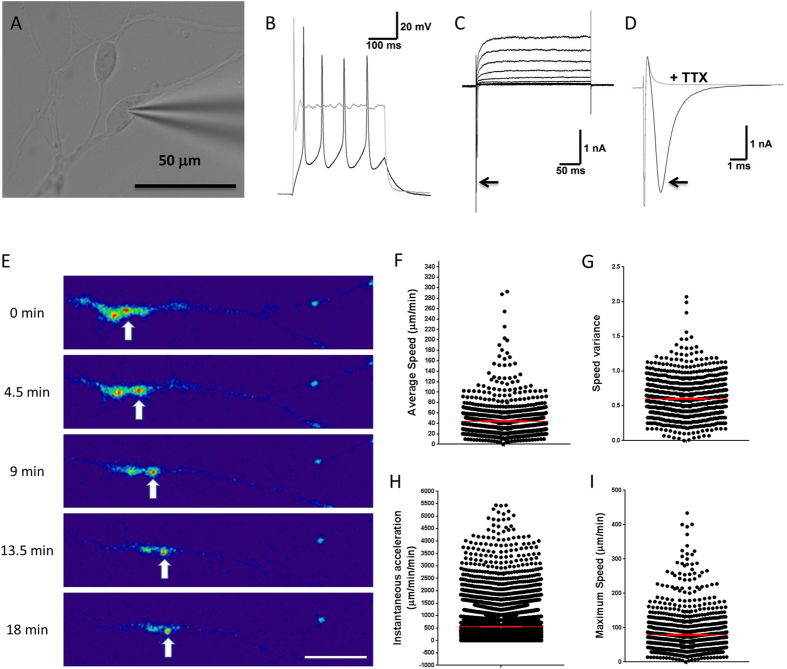
Figure 4. Electrophysiological profile and axonal transport of enriched hESC-derived RGCs.
(A) RGCs with recording microelectrode attached. (B) Typical firing profile observed in response to membrane depolarisation: multiple action potentials are evident at threshold (black trace), whilst only a single action potential is observed at higher stimulation levels (grey trace). (C) Voltage-clamp recording shows activation of inward sodium currents (arrow) followed by outward potassium currents in response to increasing membrane depolarisation. (D) The inward sodium current (arrow; black trace) is abolished in the presence of 1 mM tetrodotoxin (TTX; grey trace), a potent blocker of voltage-gated sodium channels. (E) Time-lapse images showing axonal transport of mitochondria cluster (white arrows). Scale bar = 15 μm. Quantification of (F) average speed (n = 1,049), (G) variance in speed (n = 1,049), (H) instantaneous acceleration (n = 10,606) and (I) maximum speed of mitochondria transport along axon (n = 1,049). Mean ± SEM are shown in red.