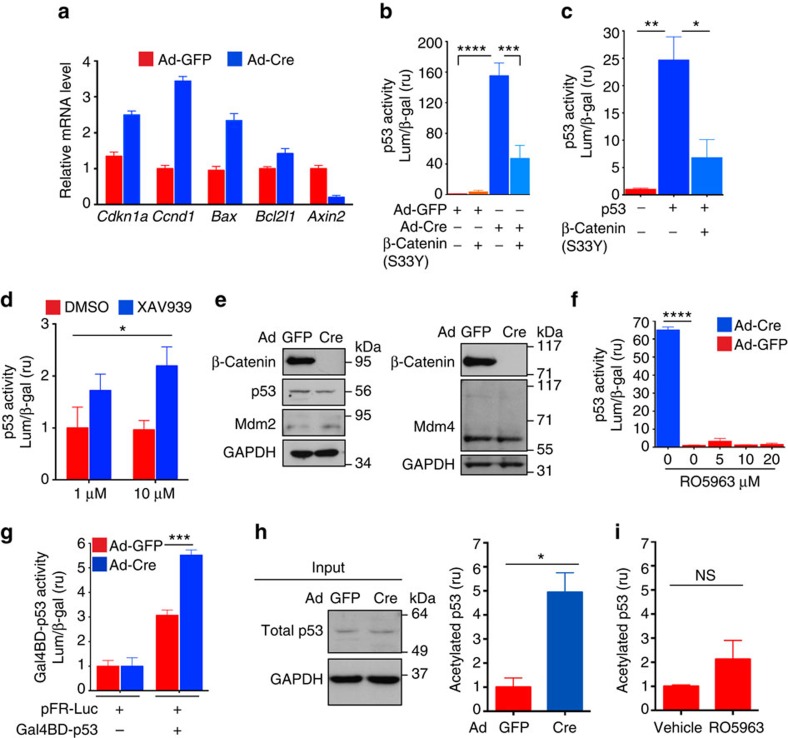
Figure 4. β-Catenin inhibits p53 acetylation and activity in vascular SMCs.
(a) RT-qPCR of indicated genes in mouse aortic SMCs, Ad-GFP (control) versus Ad-Cre (β-catenin-deficient), normalized to Rps13. Data represent the mean ±s.d., n=3. (b) p53 activity was measured with the p53 reporter, PG13-Luc plasmid, in mouse aortic SMCs. β-Catenin (S33Y), constitutively active β-catenin. Luminescence (Lum) was normalized to β-galactosidase activity (β-gal), to control for transfection efficiency. ***P<0.001; ****P<0.0001. (c) p53 activity in mouse aortic SMCs electroporated with PG13-Luc and the indicated expression vectors. *P<0.05; **P<0.01. (d) p53 activity in mouse aortic SMCs electroporated with PG13-Luc and treated with β-catenin inhibitor XAV939 or vehicle (DMSO). *P<0.05 comparing DMSO versus XAV939 by two-way ANOVA. (e) Western blot analysis of the indicated proteins in mouse aortic SMCs, Ad-GFP versus Ad-Cre. (f) p53 activity in mouse aortic SMCs electroporated with PG13-Luc, and exposed to increasing concentrations of RO5963, an Mdm2/Mdm4 inhibitor. ****P<0.0001. (g) Gal4BD-p53 transcriptional activity in mouse aortic SMCs electroporated with pFR-Luc and Gal4BD-p53 as indicated. ***P<0.001 comparing Ad-GFP versus Ad-Cre by two-way ANOVA and Sidak's multiple comparisons test. (h) Evaluation of acetylated p53 by sandwich ELISA in mouse aortic SMCs. Left: western blot analysis of total p53 in the input cell lysates. Right: levels of acetylated p53 were measured by spectrophotometric determination of absorbance at 450 nm, normalized to input and expressed as fold change of control cells. (i) Acetylated p53 was evaluated as in h, in mouse aortic SMCs treated with vehicle (DMSO) or 10 μM RO5963, an Mdm2/Mdm4 inhibitor. In h,i, *P<0.05; NS, not significant, comparisons done by two-tailed t-test. In b,c,f, comparisons done by one-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparisons test. In b–d, f–i, data represent the mean±s.e.m., and n=3.