Fig. 1.
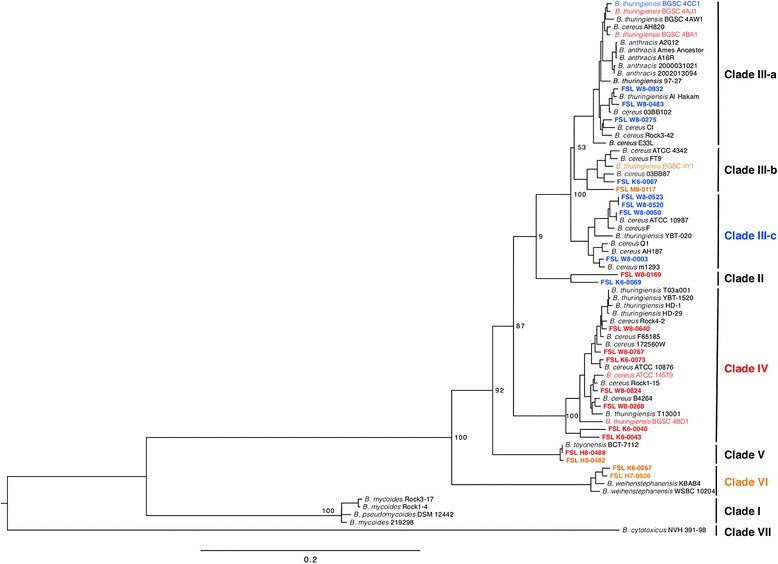
Core genome phylogeny of 69 B. cereus group isolates. Maximum likelihood tree was constructed using core genome SNPs identified with kSNP for 22 dairy-associated isolates and 47 reference isolates. Phylogeny was inferred using RaxML under general time-reversible model with gamma distributed substitution sites, and 1000 bootstrap repetitions. Bar represents 0.2 substitutions per site. WGS revealed nine B. cereus group phylogenetic clades. These clades were named according to previously proposed phylogenetic groups based on panC sequence types [33]. Where panC phylogenetic groups could be separated into different WGS clades this was clarified by the use of alphabetical subdesignation (e.g., panC group III was resolved into WGS clades III-a, III-b, and III-c). Isolates in red carried hblACD genes and produced hemolysin BL, isolates in orange carried hblACD genes, but did not produce hemolysin BL, and isolates in blue did not carry hblACD genes nor did they produce hemolysin BL. Dairy-associated isolates are in bold
