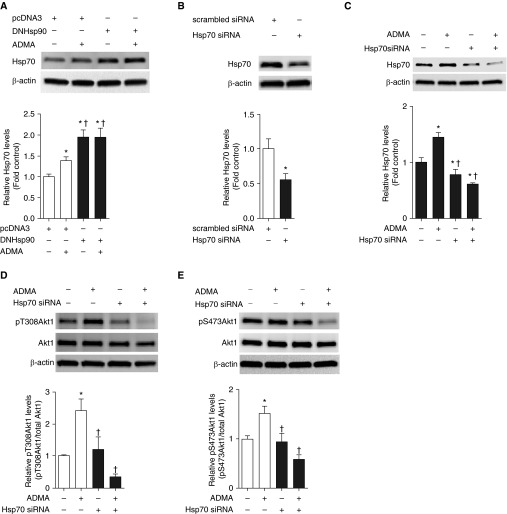
Figure 4.
Depletion of Hsp70 abolishes ADMA-mediated Akt1 phosphorylation in PAECs. PAECs were transfected with DN Hsp90 or pcDNA3 for 48 hours, followed by ADMA (10 μM, 2 h) treatment. Whole-cell lysates (20 μg) were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis to determine Hsp70 levels. A representative image is shown (A). Both ADMA and DN Hsp90 overexpression increase Hsp70 levels (A). PAECs were transiently transfected with a small interfering RNA (siRNA) for Hsp70 or a control siRNA. At 48 hours after transfection, whole-cell lysates (20 μg) were prepared and subjected to IB analysis to determine Hsp70 levels. A representative image is shown. Transfection with the Hsp70 siRNA reduces Hsp70 protein levels by approximately 50% (B). The effect of ADMA (10 μM, 2 h) on Akt1 phosphorylation at T308 and S473 after Hsp70 knockdown was then determined using duplicate blots. Representative images are shown for Hsp70 (C), T308 (D), and S473 (E). ADMA increased Hsp70 levels (C). Depleting Hsp70 protein levels (C) completely abolished ADMA-induced Akt1 phosphorylation at T308 (D) and S473 (E). Values are means (±SEM); n = 4–6. *P < 0.05 versus control siRNA; †P < 0.05 versus control siRNA with ADMA treatment.