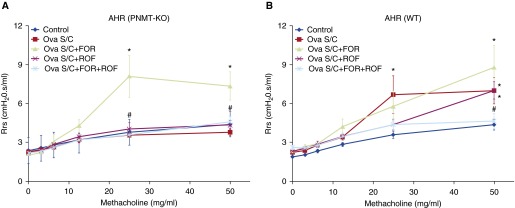
Figure 5.
Effect of ROF administration, with or without FOR coadministration, on airway resistance. (A and B) Airway resistance responses to increasing doses of nebulized methacholine (0–50 mg/ml) were measured using forced oscillation technique in Ova S/C PNMT-KO (A) and WT (B) mice administered different drug combinations. Airway resistance was determined by averaging the three highest resistance responses recorded for each mouse at each methacholine dose. In these groups of mice, ROF (5 mg/kg) was administered once daily via oral gavage or coadministered twice daily with FOR (5 μg/kg, intraperitoneally) for 12 days. Data represent the mean (±SEM) from n = 4–9 mice in each group. *P < 0.05 significance compared with respective PNMT-KO or WT CTL; #P < 0.05 significance compared with respective PNMT-KO or WT treatment groups in the absence of ROF. AHR, airway hyperresponsiveness.