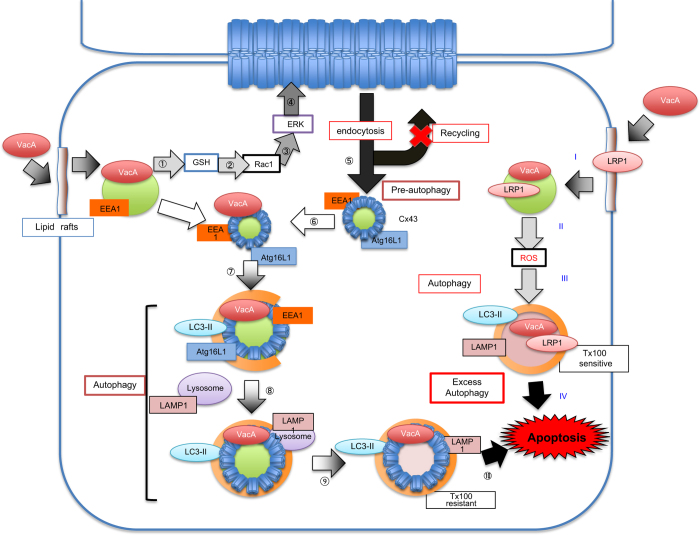
Figure 8.
Proposed model of VacA effects on Cx43 and autophagy, followed by apoptosis. After VacA was translocated into cells via a lipid raft-dependent pathway, toxin channel activity is proposed to cause dysregulated GSH metabolism and activation of Rac1, followed by ERK phosphorylation (①–④). These signaling events promote Cx43 endocytosis. Cx43 enters endosome and pre-autophagy pathways as determined by the presence of several vesicle marker proteins (e.g., LC3, Atg16L1, EEA1 and LAMP1) (⑤–⑧). Cx43 accumulated in cytoplasmic compartments and colocalized with autophagosomal marker LC3 and VacA. The cytoplasmic compartments were predominantly localized in the Tx-insoluble fraction, suggesting its localization in cholesterol-rich DRMs (⑨–⑩). In contrast, LRP1-dependent endocytosis of VacA caused ROS-dependent autophagy and apoptosis (I–IV). These compartments were localized to the Tx-soluble fraction.