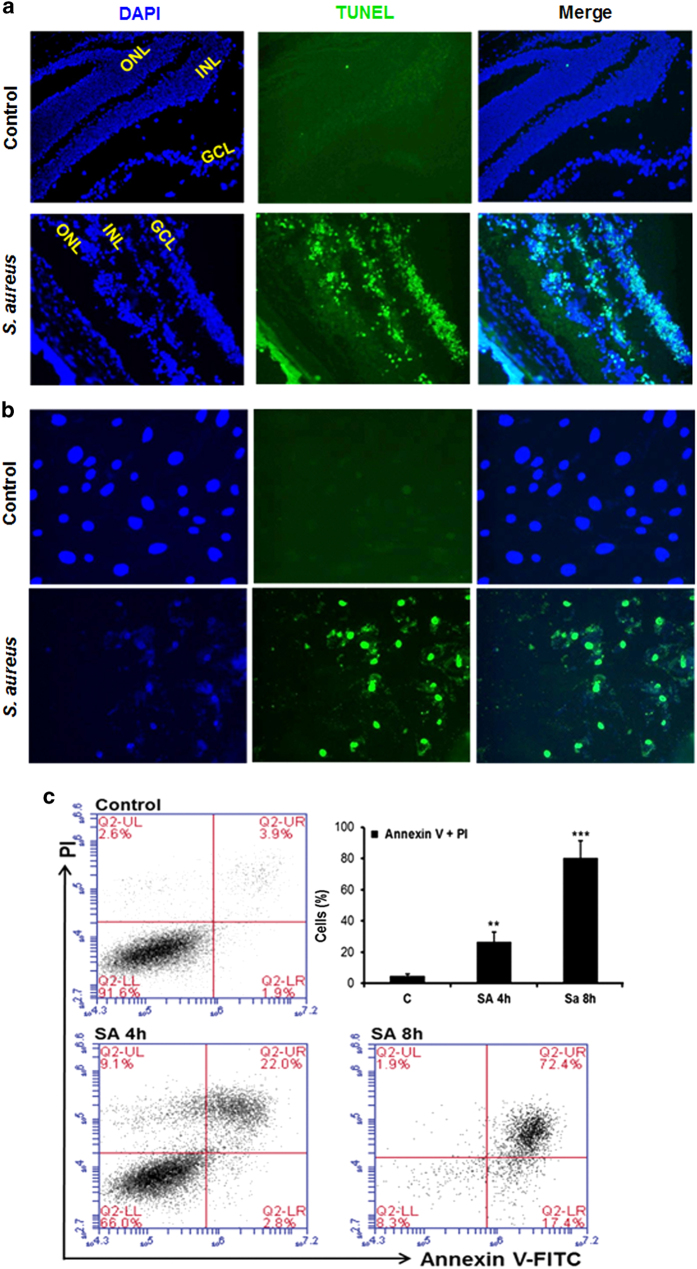
Figure 1.
S. aureus induces apoptosis in the mouse retina and retinal Müller glia. The right eyes of C57BL/6 mice (n=4) were injected intravitreally with 5000 c.f.u. of S. aureus (SA) RN6390, and the left eyes were injected with PBS (control). After 24 h, eyes were enucleated and embedded in OCT, and retinal cryosections were subjected to TUNEL staining, (blue, DAPI nuclear stain; green, TUNEL-positive cells) (a). In an in vitro experiment, human retinal Müller glia (MIO-M1 cell line) were left uninfected (control) or challenged with S. aureus for 8 h at the multiplicity of infection of 10 : 1. The control and S. aureus-infected cells were fixed, permeabilized and subjected to TUNEL staining (b). For quantitative analysis of apoptotic cells, flow cytometry was performed on Annexin V (fluorescein isothiocyanate labeled) and PI-stained MIO-M1 cells, challenged with S. aureus for the indicated time points. The bar graph represents the mean percentage of Annexin V and PI-positive cells (c). The in vitro data is a cumulative of three independent experiments performed in duplicates. **P<0.005; ***P<0.0005, t-test; GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer.