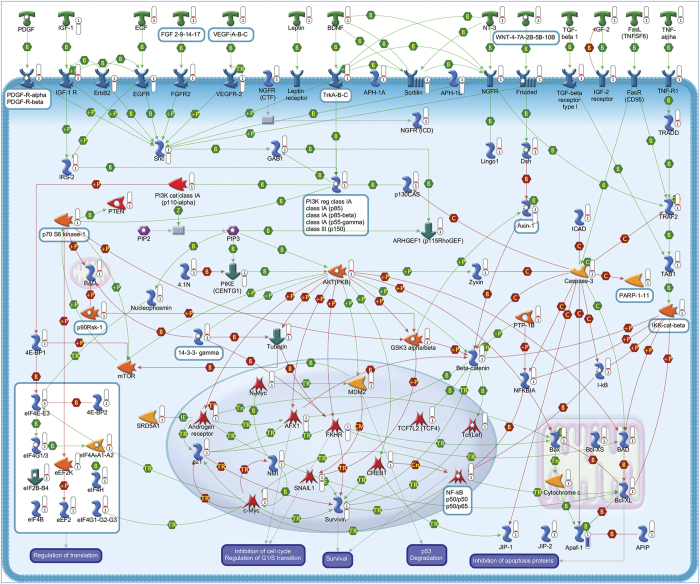
Figure 4.
PI3K-AKT (phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase-AKT) signaling pathway. The PI3K-PKB/AKT pathway is controlled by a multistep process. Activated receptors directly stimulate class 1A PI3Ks bound via their regulatory subunit or adapter molecules such as the insulin receptor substrate (IRS) proteins. This triggers activation of PI3K and conversion of PIP2 (phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate) into PIP3 (phosphatidylinositol3,4,5-trisphosphate). PKB/AKT binds to PIP3 at the plasma membrane, allowing PDK1 to activate PKB/AKT. Physiological roles of AKT include activation of protein synthesis, inhibition of apoptosis, cell cycle progression and transcription factors regulation. These are exerted by phosphorylation of a variety of downstream substrates, including caspase-3, BAX, BAD, Bcl-XL, FKHR, IKK, NF-κB, GSK3, AR, MDM2, CREB, p21, p70S6K1, JIP1 scaffold protein and a series of initiation factors. Dephosphorylation by protein phosphatase-2A (PP2A) and the conversion of PIP3 to PIP2 by PTEN antagonize AKT signaling. Pathway objects and links are described separately in Supplementary Figure 16.