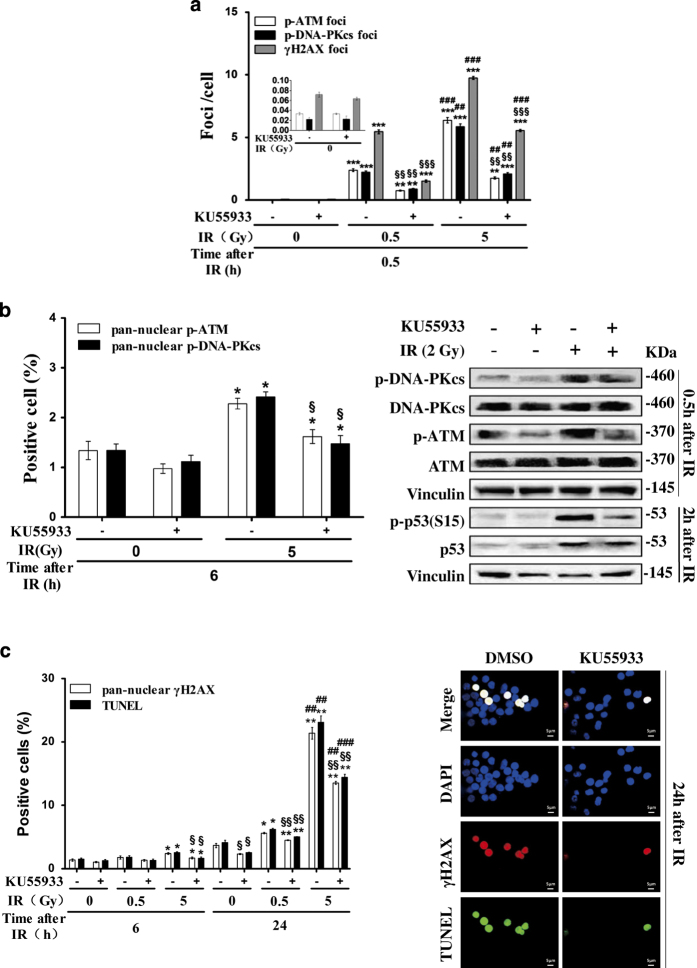
Figure 3.
Inhibition of X-irradiation-induced pan-nuclear γH2AX response and apoptosis in resting HPBLs by KU55933. (a) HPBLs were treated with 10 μM KU55933 for 2 h before X-irradiation (0.5 or 5 Gy). γH2AX, p-ATM and p-DNA-PKcs foci were measured in 500–1000 HPBLs from each sample. (b) HPBLs were treated with 10 μM KU55933 for 2 h before X-irradiation (5 Gy). Pan-nuclear p-ATM and p-DNA-PKcs cells (left panel) were counted, and western blotting assays (right panel) were performed to examine the expression of p-ATM/ATM, p-DNA-PKcs/DNA-PKcs and p-p53/p53 proteins at the indicated time points after irradiation. (c) HPBLs were treated with 10 μM KU55933 for 2 h before X-irradiation (0.5 or 5 Gy). Pan-nuclear γH2AX and TUNEL-positive cells were measured, and their representative images were captured at 24 h after X-irradiation; γH2AX was labeled in red and TUNEL in green, and nuclei were stained in blue with DAPI. A total of 2000–5000 HPBLs from each sample were examined to determine the percentage of the pan-nuclear γH2AX, p-ATM, p-DNA-PKcs and TUNEL-positive cells. ×100 magnification, ×1.0 zoom. The values shown in panel (a), panel (b) and panel (c) represent the means±S.D. obtained from three to four donors. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 compared with corresponding non-irradiated HPBLs; ## P<0.01 and ### P<0.001 compared with corresponding HPBLs exposed to 0.5 Gy X-ray irradiation with/without inhibitor treatment; § P<0.05, §§ P<0.01 and §§§ P<0.01 compared with corresponding HPBLs without inhibitor treatment.