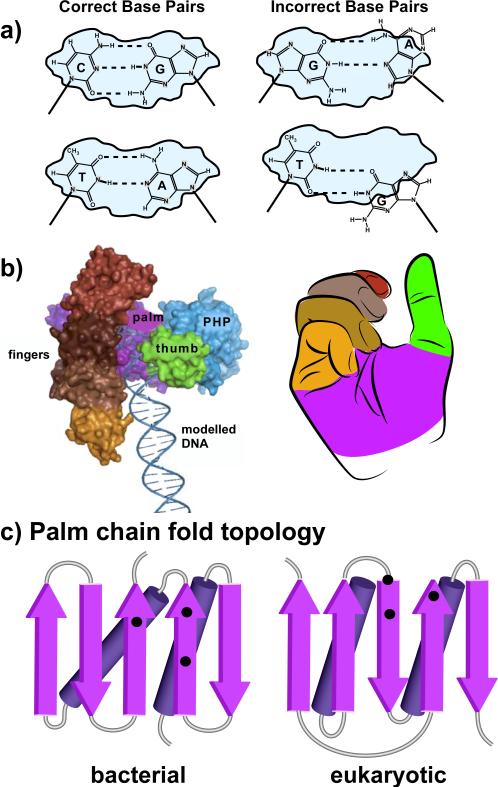
Figure 3.
Overview of DNA polymerase structure. (a) DNA polymerases match the incoming dNTP to the template strand and bury the base pair within a confined active site (gray) prior to catalysis. Only correct base pairs, GC and AT, fit the confines of the active site, thereby enabling catalysis (left diagrams). Mispairs do not fit the active site and catalysis does not occur (right diagrams). (b) DNA polymerases have the shape of a right hand. At left is a space filling model of E. coli Pol III, the chromosomal replicase (adapted with permission from Figure 5A of Lamers et al., 2006). To the right is an idealized right hand. The coloring of fingers, palm and thumb domains correspond to the colors of the analogous domains in the Pol III structure at the left. (c) Chain topology diagrams of the polypeptide chain folding pattern of the palm domains within: left, bacterial replicative polymerase (C family); right, eukaryotic replicative polymerases (B family) (see color version of this figure at www.informahealthcare.com/bmg).