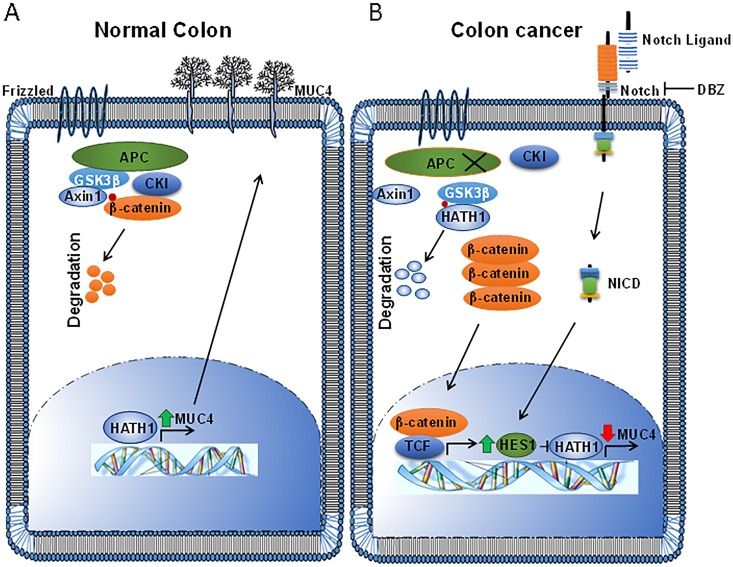
Figure 7. A schematic representation of the findings of this study.
(A) In the normal colon, Wnt signaling is inactive and Hath1 is transcriptionally active in differentiated secretory cells. Hath1 transcriptionally activates MUC4, as well as other mucins such as MUC2. (B) However, in colorectal cancer, active Wnt/β-catenin and Notch signaling transcriptionally upregulate Hes1. Hes1 antagonizes Hath1, thus reducing Hath1 levels. In addition, the Hath1 protein is targeted for phosphorylation mediated destruction by GSK3β instead of β-catenin, further reducing Hath1 levels. Thus, MUC4 is no longer actively transcribed owing to reduced Hath1, resulting in reduced MUC4.